- Title
-
Adjudin improves beta cell maturation, hepatic glucose uptake and glucose homeostasis
- Authors
- Ren, L., Charbord, J., Chu, L., Kemas, A.M., Bertuzzi, M., Mi, J., Xing, C., Lauschke, V.M., Andersson, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Diabetologia
|
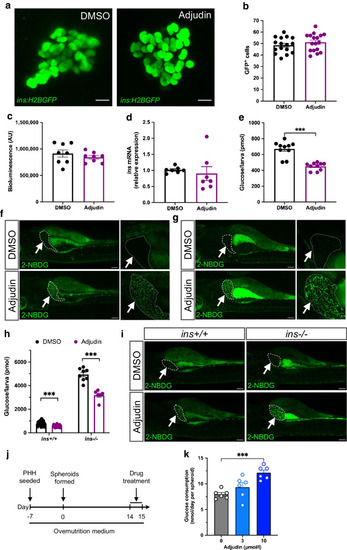
Adjudin improves the function of regenerated beta cells in zebrafish. ( |
|
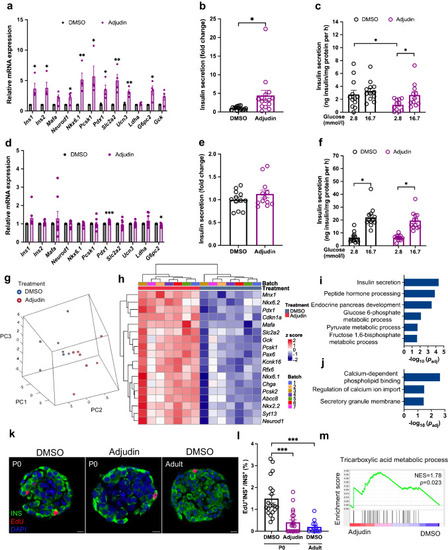
Adjudin improves the function of neonatal mouse islets. ( |
|
Adjudin improves the function of islets from |
|
Adjudin stimulates glucose uptake in the zebrafish liver and in human liver spheroids. ( |
|
Adjudin improves glucose homeostasis in |