- Title
-
Zebrafish Embryos Display Characteristic Bioelectric Signals during Early Development
- Authors
- Silic, M.R., Dong, Z., Chen, Y., Kimbrough, A., Zhang, G.
- Source
- Full text @ Cells
|
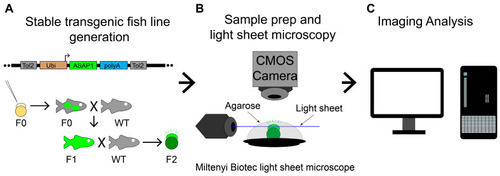
Overall experimental procedure. (A) Illustration of a Tol2 construct, the method to produce stable ASAP1 zebrafish line, Tg (ubi: ASAP1), and zebrafish crosses. X indicates fish cross. Black arrows show fish raising or producing. The green color labels the ASAP1 transgene. (B) Experimental setup to image zebrafish Tg (ubi: ASAP1) embryos with Miltenyi Biotec light sheet ultramicroscope II. ASAP1-positive embryos were mounted in agarose on a platform to keep them stable during imaging. (C) Image analysis was performed using ImageJ (v1.53e) and Imaris programs (9.7.2, Bitplane AG). |
|
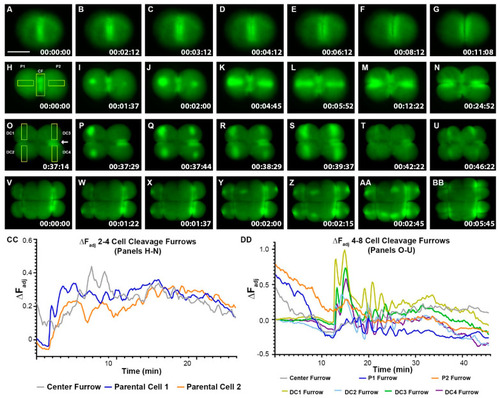
Zebrafish Cleavage period embryos display furrow-related dynamic hyperpolarization. ( |
|
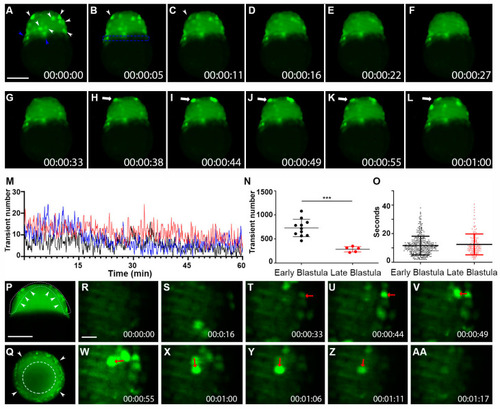
Whole-cell Vm transients occurred in the zebrafish superficial blastomeres during the blastula period. ( |
|
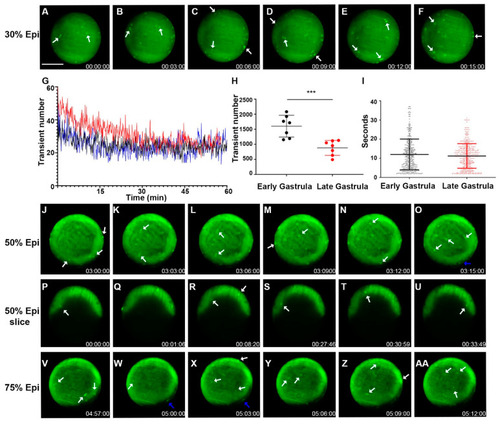
Zebrafish gastrulation exhibited whole-cell transient hyperpolarization in both superficial and deep cells. Early stage gastrula (30%) to 75% epiboly stages of the Tg ( |
|
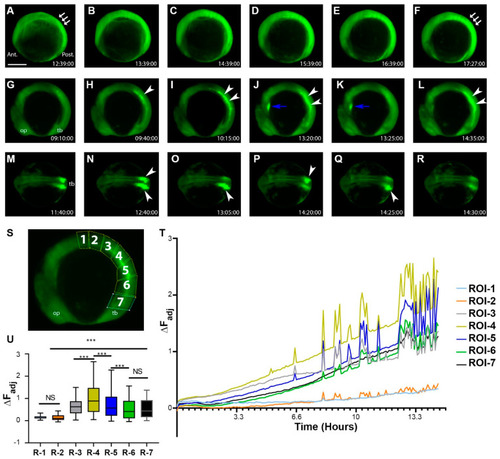
During the segment period, more complex and dynamic cellular bioelectric signals occurred at the tissue level. ( |
|
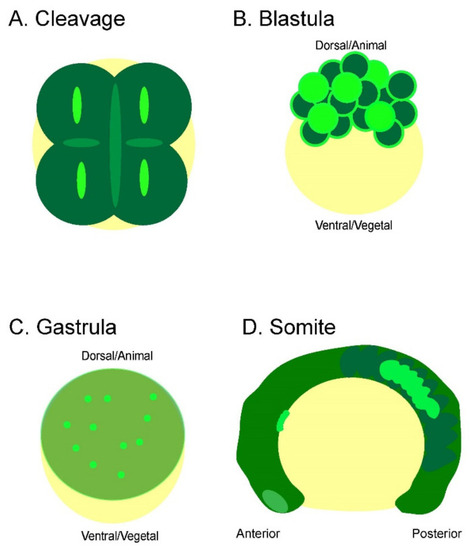
Summary of bioelectric signaling during zebrafish embryogenesis. Each early embryonic zebrafish developmental period has distinct yet overlapping bioelectricity signals and/or patterns. ( |