- Title
-
Arabinogalactan enhances Mycobacterium marinum virulence by suppressing host innate immune responses
- Authors
- Li, Y.Y., Liu, H.M., Wang, D., Lu, Y., Ding, C., Zhou, L.S., Wu, X.Y., Zhou, Z.W., Xu, S.Q., Lin, C., Qin, L.H., Li, Y., Liu, J., Liu, H.P., Zhang, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
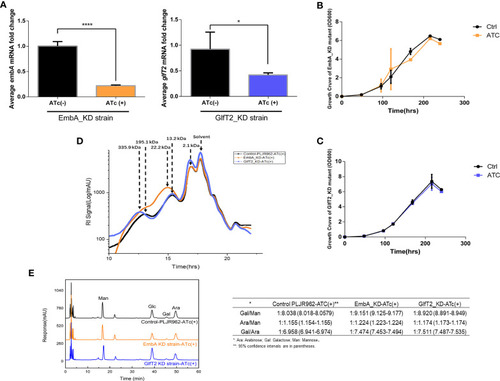
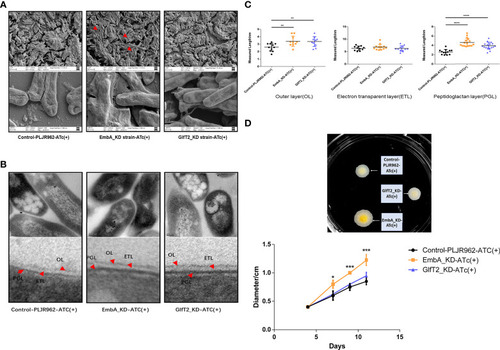
Construction of conditional EmbA/GlfT2_KD strains and validation of impaired arabinogalactan synthesis in |
|
Cell wall structure of knock-down strains in the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) fields. |
|
EmbA/GlfT2_KD strain-infected murine macrophage J774A.1 line. |
|
Zebrafish infection model with EmbA/GlfT2_KD strains. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
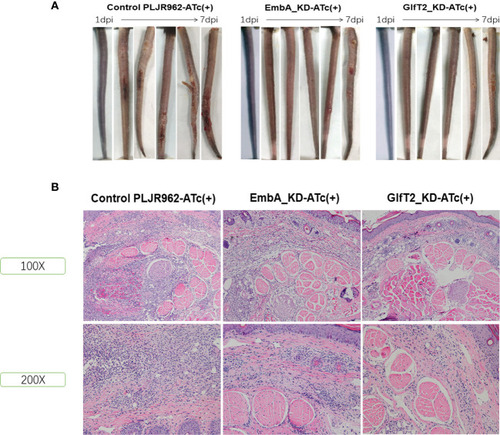
Murine tail infection model with EmbA/GlfT2_KD strains. |
|
Transcriptome analysis of EmbA/GlfT2_KD strain-infected murine macrophage line J774A.1 (MOI = 5, 12 h). |
|
Validation of |