- Title
-
Immunoprotective Effects of Two Histone H2A Variants in the Grass Carp Against Flavobacterium columnare Infection
- Authors
- Yang, Y.Y., Zheng, S.Y., Fang, H., Wu, X.M., Zhang, J., Chang, M.X.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
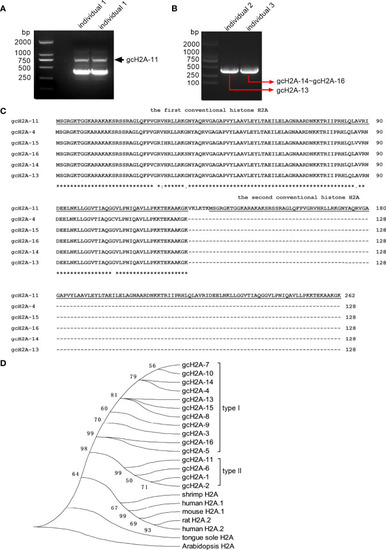
The cloning and sequence analysis of grass carp histone H2A variants. |
|
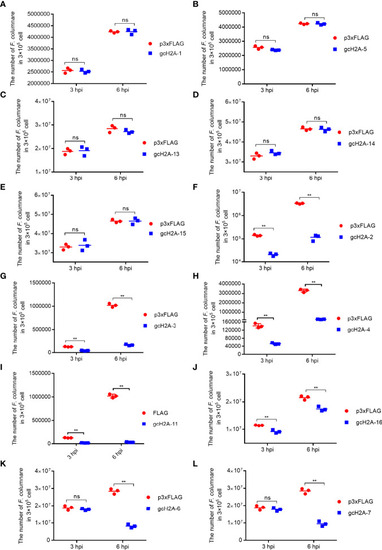
The effects of grass carp histone H2A variants in bacterial infection. |
|
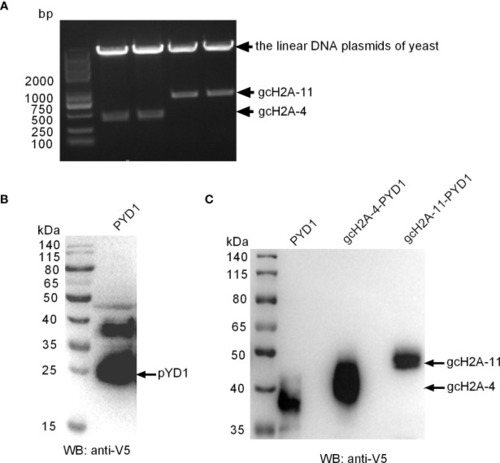
The recombinant expressions of gcH2A-4 and gcH2A-11 in the |
|
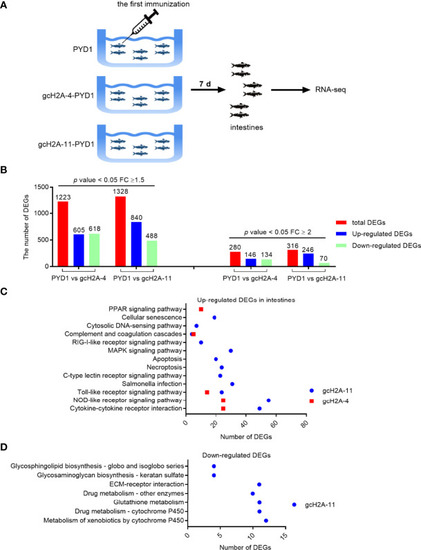
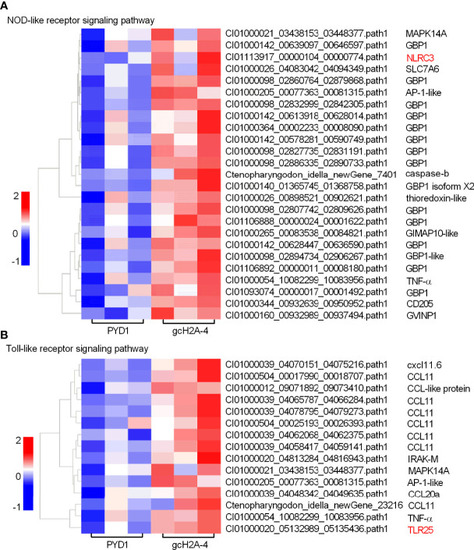
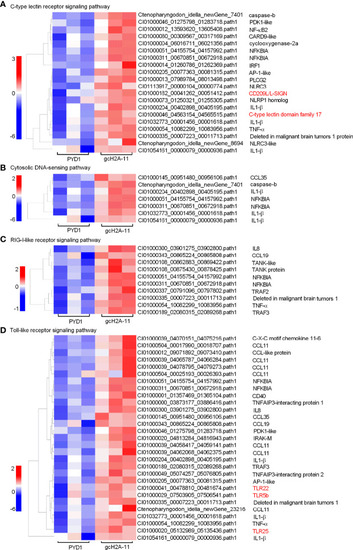
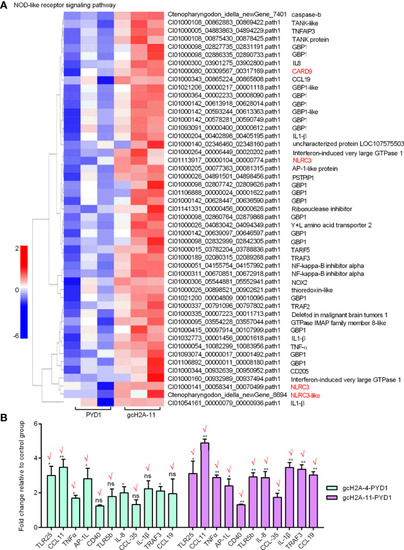
Differentially expressed genes and significantly enriched KEGG pathways in grass carp regulated by the engineered |
|
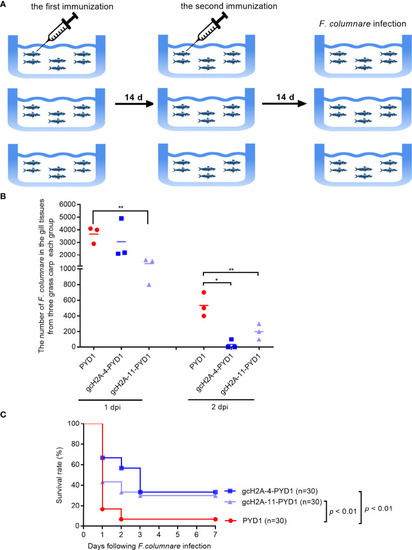
The effects of the engineered |
|
The effects of the engineered |
|
Validation of transcriptome data by qRT-PCR. |
|
The effects of the engineered |