- Title
-
Zebrafish Establish Female Germ Cell Identity by Advancing Cell Proliferation and Meiosis
- Authors
- Pan, Y.J., Tong, S.K., Hsu, C.W., Weng, J.H., Chung, B.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
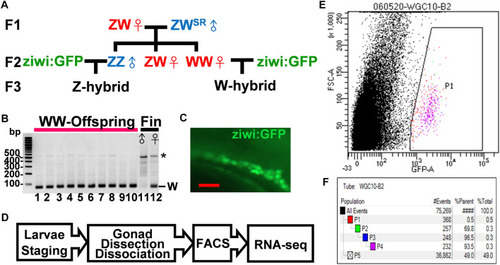
Isolation of germ cells from juvenile zebrafish with defined sex. |
|
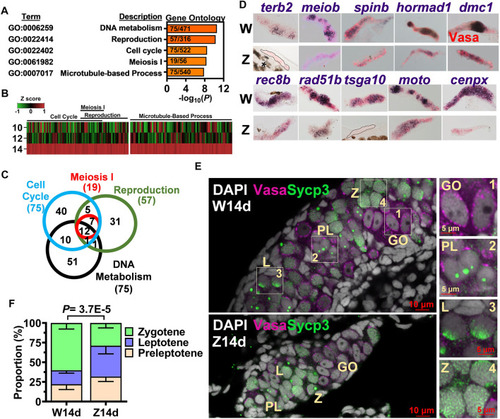
Meiosis as the hallmark of 14-dpf female germ cell transcriptome. |
|
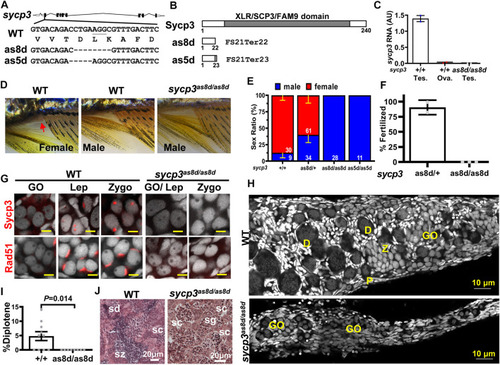
Disruption of sycp3 leads to infertile males with germ cell arrest during meiosis. |
|
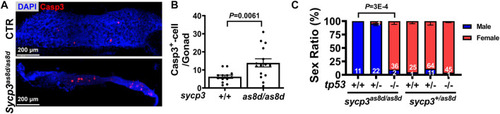
The sex reversal of sycp3 mutant fish is caused by germ cell apoptosis and can be compensated by additional tp53 mutation. |
|
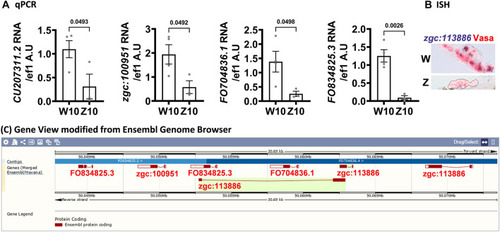
Genes clustered on chromosome 17 are upregulated in 10-dpf germ cells of the W-hybrid. |
|
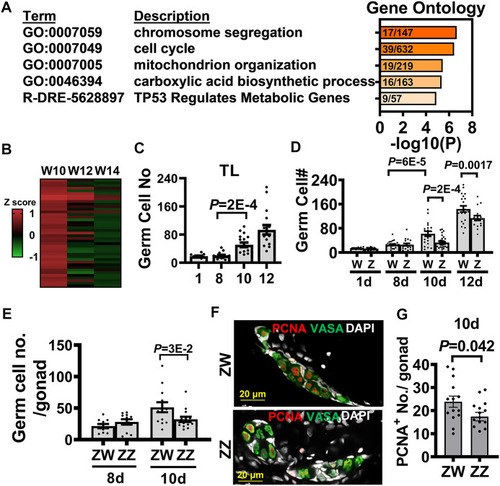
Transcriptome analysis of 10-dpf germ cells identifies the advanced germ cell proliferation as a sign of zebrafish female differentiation. |