- Title
-
From the North Sea to Drug Repurposing, the Antiseizure Activity of Halimide and Plinabulin
- Authors
- Copmans, D., Kildgaard, S., Roux, E., Partoens, M., Steurs, G., Wang, X., De Borggraeve, W.M., Esguerra, C.V., Crawford, A.D., Larsen, T.O., de Witte, P.A.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Pharmaceuticals (Basel)
|
Bioactivity-guided identification of the active compound halimide of antiseizure hit SK0107. (A) Aspergillus insuetus IBT 28443 cultivated on czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) and yeast extract sucrose agar (YES) media for 9 days at 25 °C in the dark. Base peak chromatograms (BPC) of the crude extract and bioactive fraction SK0107 in positive electrospray ionization mode (ESI+). (B) Aspergillus insuetus IBT 28443 cultivated on CYA media for 9 days at 25 °C in the dark. ESI+ BPC chromatograms of the most bioactive fraction (SK1312) from first reversed-phase fractionation and of the two most bioactive fractions (SK1414 and SK1415) from the second reversed-phase fractionation. UV/Vis and HRMS spectra shown for halimide (I). TMC-120A (II) and TMC-120B (III) peaks are also indicated. (C–F) Antiseizure activity of SK0107 (means are pooled from three independent experiments with 12 replicate wells per condition each) (C), SK1312 (n = 23–24 replicate wells per condition) (D), SK1414 (n = 10–11 replicate wells per condition) (E), and SK1415 (n = 22 replicate wells per condition) (F) in the zebrafish pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure model after 2 h of treatment. Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min (±SEM) during the 30 min recording period. Statistical analysis: (C–F) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (GraphPad Prism 5, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001. Abbreviation: vehicle: VHC. |
|
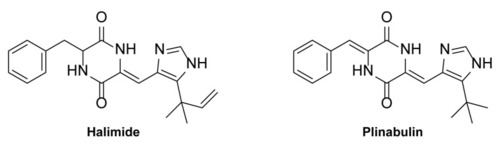
Chemical structures of the 2,5-diketopiperazine halimide and commercially available structural analogue plinabulin. |
|
Antiseizure and anti-epileptiform analysis of halimide in the zebrafish PTZ seizure model. Antiseizure activity (A,B) and anti-epileptiform activity (C,D) of halimide in the zebrafish pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure model after 2 h of incubation. (A,B) Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min (±SEM) during the 30 min recording period (A) and over consecutive time intervals (B). Data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + PTZ control condition (B). (C,D) PTZ-induced epileptiform brain activity and the anti-epileptiform effect of 200 µg/mL halimide recorded via non-invasive local field potential recordings. Electrophysiological data is normalized against the VHC + VHC control condition and expressed as normalized power spectral density (PSD) (mean ± SEM) per larva within the 20–90 Hz region (C) and as normalized PSD (mean ± SEM) per larva per 10 Hz frequency band from 1–150 Hz (D). (A,B) Data are pooled from five independent experiments with each 6–11 replicate wells per condition: VHC + PTZ (n = 53), compound + PTZ (n = 52–53), VHC + VHC (n = 53), and compound + VHC (n = 41). (C,D) Number of replicates per condition: VHC + PTZ (n = 17), VHC + VHC (n = 13), halimide + PTZ (n = 11) and halimide + VHC (n = 12). Statistical analysis: (A,C) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, (B,D) two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, (C,D) outliers were removed via the ROUT test (Q = 1%) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
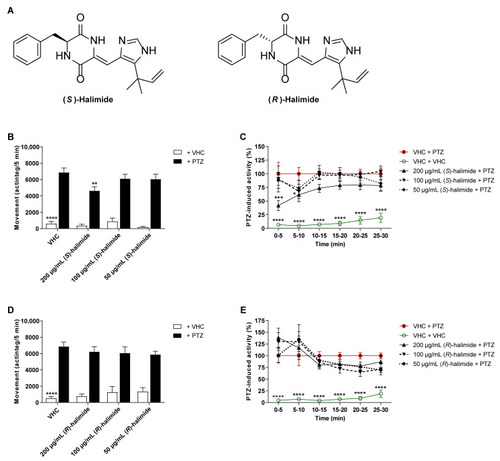
Behavioral antiseizure analysis of the R- and S-enantiomers of halimide in the zebrafish PTZ seizure model. (A) Chemical structures of (S)-halimide and (R)-halimide. (B–E) Antiseizure activity of (S)-halimide (B,C) and (R)-halimide (D,E) in the zebrafish pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure model after 2 h of incubation. Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min (±SEM) during the 30 min recording period (B,D) and over consecutive time intervals (C,E). Data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + PTZ control condition (C,E). Data are pooled from two independent experiments with a total of 20 replicate wells for VHC + VHC, VHC + PTZ, and compound + PTZ conditions, and 11–12 replicate wells for compound + VHC conditions. Statistical analysis: (B,D) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, (C,E) two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
Behavioral antiseizure analysis of plinabulin after a short- and long-term treatment in the zebrafish PTZ seizure model. Antiseizure activity of plinabulin in the zebrafish pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure model after a treatment period of 2 h (A,B) and 18 h (C,D). Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min (±SEM) during the 30 min recording period (A,C) and over consecutive 5 min time intervals (B,D). Data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + PTZ control condition (B,D). Data were pooled from ten independent experiments with 10 replicate wells per test condition (n = 100 for VHC + VHC and VHC + PTZ and n = 70 for plinabulin + VHC and plinabulin + PTZ) (A,B), and from three independent experiments with 10 replicate wells per test condition (n = 30) (C,D). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A,C), two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (B,D) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
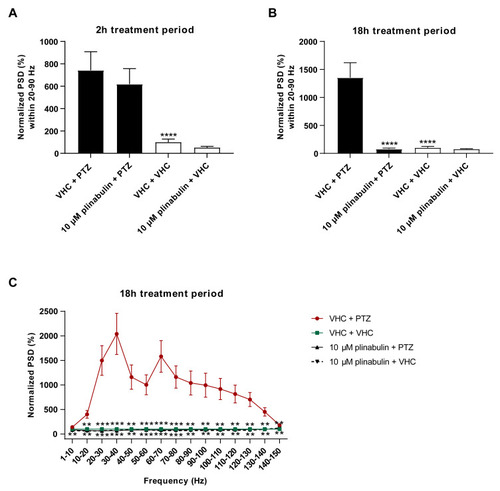
Electrophysiological antiseizure analysis of plinabulin in the zebrafish PTZ seizure model after a short- and long-term treatment. Anti-epileptiform activity of plinabulin after 2 h (A) and 18 h (B,C) in the zebrafish pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizure model. Electrophysiological data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + VHC control condition and expressed as normalized power spectral density (PSD) (mean ± SEM) per larva within the 20–90 Hz region (A,B) and as normalized PSD (mean ± SEM) per larva per 10 Hz frequency band from 1–150 Hz (C). Number of replicates per test condition was n = 12–17. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A,B), two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (C), outliers were removed via the ROUT test (Q = 1%) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
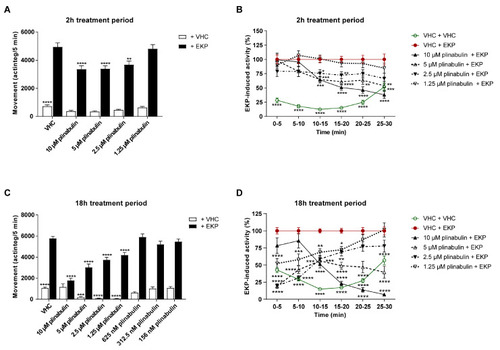
Behavioral antiseizure analysis of plinabulin after short- and long-term treatment in the zebrafish EKP seizure model. Antiseizure activity of plinabulin in the zebrafish ethyl ketopentenoate (EKP) seizure model after a treatment of 2 h (A,B) and after a treatment of 18 h (C,D). Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min intervals (±SEM) during the 10–25 min recording period (A,C) and over consecutive 5 min time intervals during the entire 30 min recording period (B,D). Data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + EKP control condition (B,D). Data were pooled from four independent experiments with 10 replicate wells per test condition (n = 40) (A,B) and from three or four independent experiments with 10 replicate wells per test condition (n = 70 for VHC + VHC and VHC + EKP, n = 28–30 for 5–10 µM plinabulin conditions, and n = 39–40 for 0.156–2.5 µM plinabulin conditions) (C,D). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A,C), two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (B,D) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
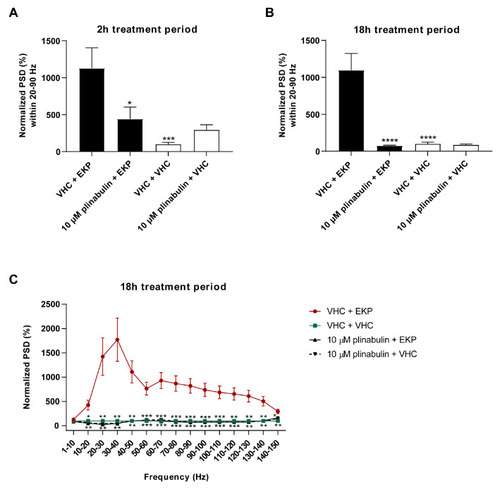
Electrophysiological antiseizure analysis of plinabulin in the zebrafish EKP seizure model after a short- and long-term treatment. Anti-epileptiform activity of plinabulin after 2 h (A) and 18 h (B,C) in the zebrafish ethyl ketopentenoate (EKP) seizure model. Electrophysiological data is normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + VHC control condition and expressed as normalized power spectral density (PSD) (mean ± SEM) per larva within the 20–90 Hz region (A,B) and as normalized PSD (mean ± SEM) per larva per 10 Hz frequency band from 1–150 Hz (C). Number of replicates per test condition was n = 13–16. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A,B), two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (C), outliers were removed via the ROUT test (Q = 1%) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
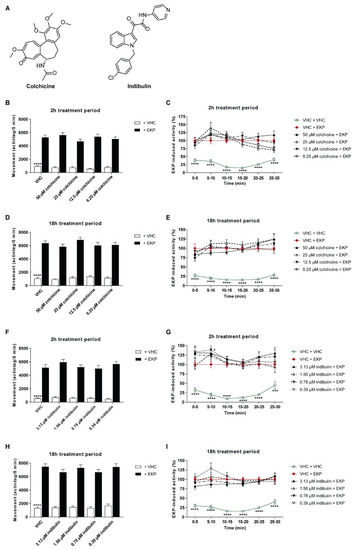
Behavioral antiseizure analysis of colchicine and indibulin in the zebrafish EKP seizure model after short- and long-term treatment. (A) Chemical structures of colchicine and indibulin. (B–I) Antiseizure activity of colchicine (B–E) and indibulin (F–I) after a treatment of 2 h (B,C,F,G) and after a treatment of 18 h (D,E,H,I) in the zebrafish ethyl ketopentenoate (EKP) seizure model. Behavioral data is expressed in mean actinteg units per 5 min (±SEM) during the 10–25 min recording period (B,D,F,H), and over consecutive 5 min time intervals during the entire 30 min recording period (C,E,G,I). Data are normalized against the vehicle (VHC) + EKP control condition (C,E,G,I). Data were pooled from three independent experiments with 10 replicate wells per test condition (n = 30) (B–I). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (B,D,F,H), two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (C,E,G,I) (GraphPad Prism 9, San Diego, CA, USA). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001. |
|
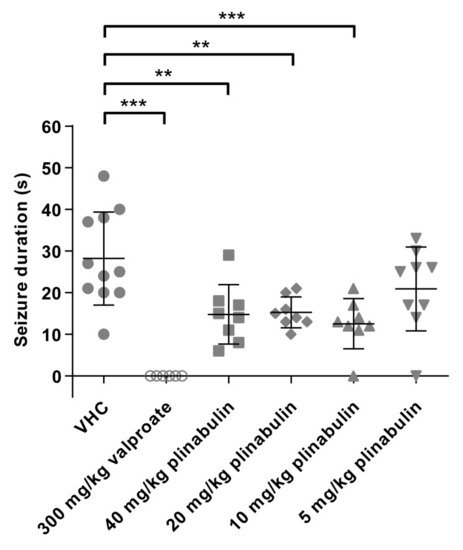
Antiseizure activity analysis of plinabulin in the mouse 6 Hz psychomotor seizure model. Drug-resistant psychomotor seizures were induced by electrical stimulation (6 Hz, 0.2 ms rectangular pulse width, 3 s duration, 44 mA) through the cornea, 30 min after intraperitoneal injection of vehicle (VHC, n = 11), positive control valproate (n = 6), or plinabulin (n = 8–9). Mean seizure durations (±SD) are depicted. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (GraphPad Prism 9). Significance levels: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001. |
|
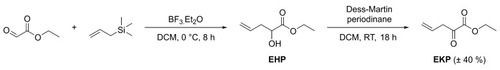
Synthesis of ethyl ketopentenoate (EKP) via Lewis acid-catalyzed allylation of ethyl glyoxylate followed by Dess-Martin oxidation. Abbreviations: dichloromethane: DCM; ethyl hydroxypentenoate: EHP; 3-oxo-1λ5-benzo[d][1,2]iodaoxole-1,1,1(3H)-triyl triacetate: Dess-Martin periodinane; and room temperature: RT. |