- Title
-
Stapling of Peptides Potentiates the Antibiotic Treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii In Vivo
- Authors
- Schouten, G.K., Paulussen, F.M., Kuipers, O.P., Bitter, W., Grossmann, T.N., van Ulsen, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Antibiotics (Basel)
|
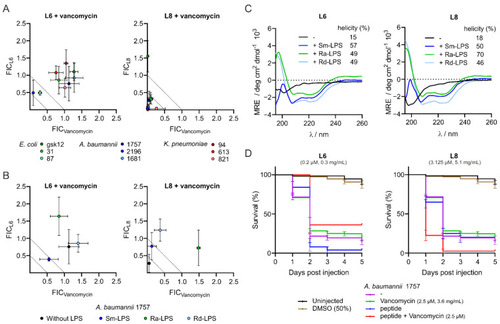
Peptides L6 and L8 are active in vitro against Gram-negative clinical isolates and interact with LPS but have limited activity in vivo. In vitro MIC values of peptides or vancomycin alone and MIC values of peptides combined with vancomycin or vancomycin in combination with peptides against Gram-negative bacteria were determined via checkerboard assays either in medium containing no LPS (A) or in medium containing smooth (Sm) LPS, rough (Ra) LPS or deep rough (Rd) LPS (B). The FIC values were defined as the ratio of either the MIC value of the peptide in combination with vancomycin over the MIC value of the peptide alone (FICL6 and FICL8) or the ratio of the MIC value of vancomycin combined with peptide over the MIC value of vancomycin alone (FICVancomycin). The degree of α-helicity of L6 and L8 either in medium containing no LPS, Sm-LPS, Ra-LPS or Rd-LPS was determined with CD spectroscopy. Relative helicity was calculated using circular dichroism analysis using neural networks (CDNN) software (C). Zebrafish larvae survival rates after infection with A. baumannii 1757 and treatment with peptides, vancomycin or combinations of peptide and vancomycin via caudal vein injection (D). The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. |
|
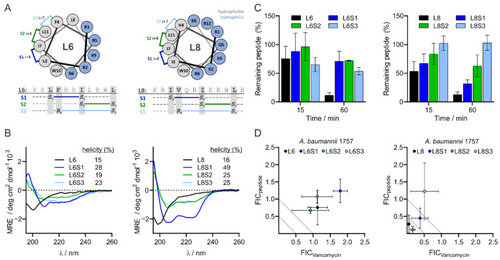
Design and properties of L6 and L8 as well as stapled versions. Design and structure of stapled L6 and stapled L8 (A). The degree of α-helicity of L6, L8 and the stapled variants of the peptides was determined with CD spectroscopy. Relative helicity was calculated using circular dichroism analysis using neural networks (CDNN) software (B). Stability of L6, L8 and the stapled variants of the peptides in human serum were analyzed by LCMS and quantified using total ion count (TIC) of selected molecular ions (C). MIC values of the stapled peptides or vancomycin alone and MIC values of the stapled peptides combined with vancomycin or vancomycin in combination with the stapled peptides against Gram-negative bacteria were determined via checkerboard assay. The FIC values were defined as the ratio of either the MIC value of the stapled peptide in combination with vancomycin over the MIC value of the stapled peptide alone (FICL6 and FICL8), or the ratio of the MIC value of vancomycin combined with the stapled peptide over the MIC value of vancomycin alone (FICVancomycin) (D). The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. |
|
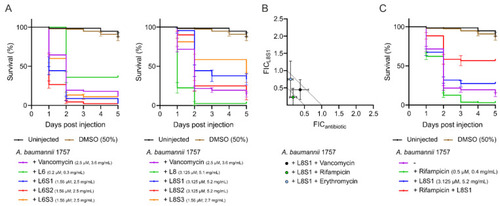
Peptide L8S1 is active in combination with vancomycin or rifampicin against A. baumannii in vivo. Zebrafish larvae survival rates were tracked over time following A. baumannii infection and treatment with stapled peptides, vancomycin or combinations of stapled peptide and vancomycin via caudal vein injection (A). MIC values of L8S1, rifampicin or erythromycin, MIC values of L8S1 combined with either rifampicin or erythromycin and MIC values of rifampicin or erythromycin combined with L8S1 were determined via checkerboard assay. The FIC values were defined as either the ratio of L8S1 in combination with rifampicin or erythromycin over the MIC value of L8S1 alone (FICL8S1), or the ratio of the MIC value of rifampicin or erythromycin combined with L8S1 over the MIC value of rifampicin or erythromycin alone (FICantibiotic) (B). Survival rates of A. baumannii infected zebrafish larvae were additionally followed upon treatment with peptide L11S1, rifampicin or a combination of L11S1 and rifampicin (C). The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. |