- Title
-
Pre-injection of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) tnfb Polyclonal Antibody Decreases the Mortality of Vibrio vulnificus Infected Zebrafish
- Authors
- Li, S., Jiang, C., Chen, H., Zhang, L., Ke, L., Chen, X., Lin, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Vet Sci
|
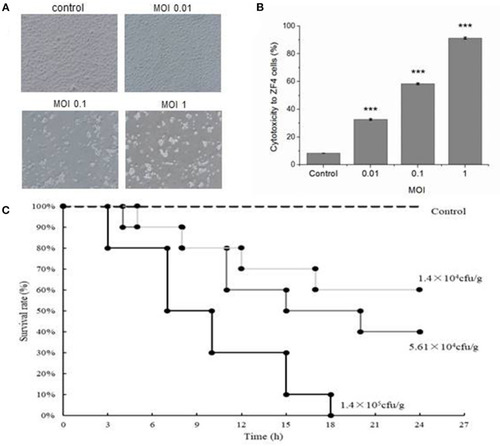
Cytotoxicity to ZF4 cells and lethality to zebrafish infected by Vibrio vulnificus. (A) The growth status of ZF4 cells under different multiplicity of infection (MOI) conditions. The cells were healthy in the control group; the cells were significantly shrunken when MOI was 0.01; the cells were severely apoptotic when MOI was 0.1; the cells were totally dead when MOI was 1. (B) The cytotoxicity to ZF4 cells under different MOI conditions. (C) The survival rate of zebrafish infected with different doses of V. vulnificus. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (SE) from three independent experiments. ***indicates significant difference at P < 0.001. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
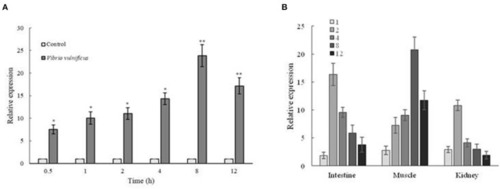
Expression analysis of Zetnf-b in ZF4 cells and zebrafish both infected by Vibrio vulnificus. (A) Expression profile of Zetnf-b using qRT-PCR in ZF4 cells infected with 0.1 MOI V. vulnificus. (B) Tissue expression of Zetnf-b using qRT-PCR in zebrafish infected with V. vulnificus. Total RNA was extracted from the cells, and qRT-PCR was conducted to analyze Zetnf-b and β-actin gene expression at 1 h post-stimulation (1 hpi), 2, 4, 8 and 12 hpi. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (SE) from three independent experiments. * indicates significant difference at P < 0.05. ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01. |
|
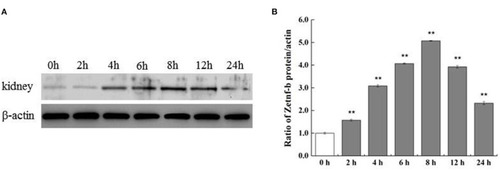
Western blotting of Zetnf-b protein in kidney of zebrafish infected by V. vulnificus at different time points. (A) Western blotting of Zetnf-b protein in the kidney of zebrafish infected by V. vulnificus at different time points. Kidney of mock-infected zebrafish was marked as “0 h” and used as the control. Polyclonal antibody of Zetnf-b (1:1,000) and rabbit polyclonal anti-β-actin (1:1,000) were used as the primary antibody. (B) The ratio of Zetnf-b protein/actin. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (SE) from three independent experiments. ** Indicate significant difference at **P < 0.01. |
|
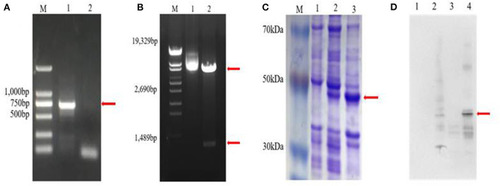
Cloning and expression of Zetnf-b. (A) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of Zetnf-b (M: DL2000 marker. 1: complementary DNA (cDNA) template. 2: sterile water negative control). (B) Double digestion results of recombinant plasmid pET32a-Zetnfb (M: λ-EcoT14 I digest. 1: recombinant plasmid pET32a-Zetnfb. 2: recombinant plasmid pET32a-Zetnfb double digestion [upper 5900 bp, lower 729 bp)]. (C) Expression of rZetnfb (M: low molecular weight pre-stained marker. 1: pET32a-Zetnfb; not induced. 2: pET32a-Zetnfb induced supernatant. 3: pET32a-Zetnfb induced precipitation). (D) Western blotting of Zetnf-b polyclonal antibody (1: pET32a; no-load not induced. 2: pET32a; no-load induced. 3: pET32a-Zetnfb; not induced. 4: pET32a-Zetnfb; induced). |
|
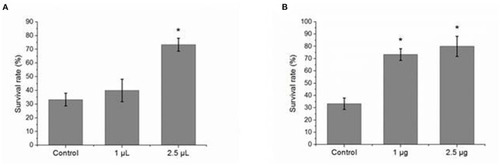
Effect of pre-injected Zetnf-b polyclonal antibody or AG-126 to zebrafish before challenging with Vibrio vulnificus. (A) The effect of pre-injection of a certain dose of Zetnf-b polyclonal antibody on the survival rate before challenging with V. vulnificus, using pre-immune rat serum as control. The survival rate was 73.3% at the dose of 2.5 μl/tail. (B) The effect of pre-injection of a certain dose of AG-126 on the survival rate before challenging with V. vulnificus, using phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) as control. The survival rate was 80% at the dose of 2.5 μg/tail. Zebrafish survival rate was calculated according to the formula. Survival rate %=(Survived zebrafish / Total fish) × 100%. Data are presented as mean ± standard error (SE) from three independent experiments. * Indicates significant difference at P < 0.05. |