- Title
-
Cartilage Acidic Protein a Novel Therapeutic Factor to Improve Skin Damage Repair?
- Authors
- Félix, R.C., Anjos, L., Costa, R.A., Letsiou, S., Power, D.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Mar. Drugs
|
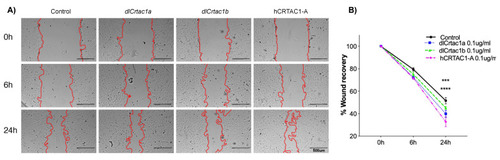
SJD.1 fibroblast scratch assay: (A) Representative images showing the progression of the scratch closure across time in control and cartilage acidic protein 1 (CRTAC1) (dlcrtac1a, dlcrtac1b and hCRTAC1-A) exposed fibroblasts. The scratch repaired more rapidly in the CRTAC1 exposed cells. Photos were taken with a Leica DM IL microscope coupled to a Visicam HDMI 6 digital camera (magnification × 4). Scale bars indicate 500 μm; and (B) scratch recovery area (percentage) was measured at 0 h, 6 h and 24 h in relation to the area immediately after the scratch (100%). The results are shown as the average ± SEM of five independent experiments with two technical replicates. The data were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism version 7.0a. p < 0.0001 (****) and p < 0.0005 (***) were considered significant. |
|
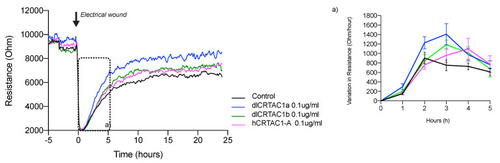
Electrical resistance of the confluent SJD.1 cell monolayer after scratching with an electrical discharge. A representative trace of the recovery of cell resistance after an electrical wound/ scratch (indicated by the arrow) is presented at 4 kHz. Changes in resistance are presented in different colors for each group of treated cells: control cells (black); hCRTAC1-A (pink), dlCrtac1a (blue) and dlCrtac1b (green). For each experimental group, the variation in resistance during the exponential phase of cell recovery (between 0 h–5 h after the wound/scratch) was estimated and is presented in insert (a). Data are presented as the average resistance of at least three independent experiments performed with two / three replicates for each experimental group. |
|
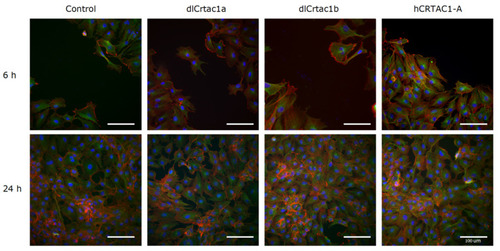
IF of SJD.1 after creating scratches in the confluent cells and treating them with CRTAC1 proteins (dlCrtac1a, dlCrtac1b and hCRTAC1-A) compared with the control cells. Colocalization of α-tubulin (green-fluorescence), F-actin (red fluorescence) and DAPI (nuclei, blue fluorescence). Images are representative of control cells, and CRTAC1 treated cells at 6 h and 24 h after scratching the confluent cell layer. Images were obtained with a Leica DM IL microscope coupled to a Visicam PRO 20C digital camera and photographs were analyzed using ImageJ software for image overlay. Scale bars indicate 100 μm. |
|
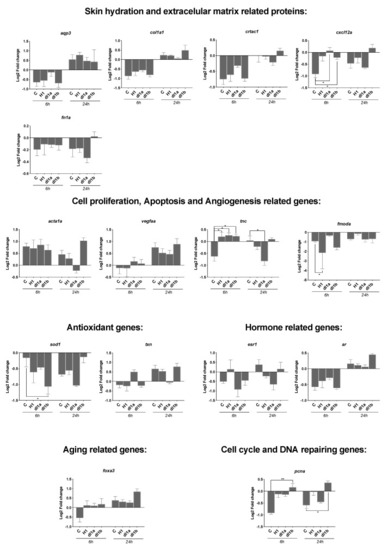
Transcript level of 15 genes quantified by RT-qPCR in SJD.1 fibroblast cells exposed to three control and CRTAC1 proteins (hCRTAC1-A, dlcrtac1a and dlcrtac1b). In intact cells (control) no damage was inflicted and other samples were collected immediately after the scratch (AS_0h) or at 6 h (AS_6h) and 24 h (AS_24h) after the scratch. Data corresponded to the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments for the control and dlCrtac1a and three independent experiments for hCRTAC1-A and dlCrtac1b. Gene expression levels (2−ΔΔCT) were normalized in relation to intact cells using the geometric mean of two reference genes (18S and ef1α) and the data were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism version 7.0a. p < 0.05 (*) and p < 0.01 (**) were considered significant. Gene symbols are indicated, for the full gene name consult Table 1. |