- Title
-
A Zebrafish Model of Metastatic Colonization Pinpoints Cellular Mechanisms of Circulating Tumor Cell Extravasation
- Authors
- Allen, T.A., Cullen, M.M., Hawkey, N., Mochizuki, H., Nguyen, L., Schechter, E., Borst, L., Yoder, J.A., Freedman, J.A., Patierno, S.R., Cheng, K., Eward, W.C., Somarelli, J.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Oncol
|
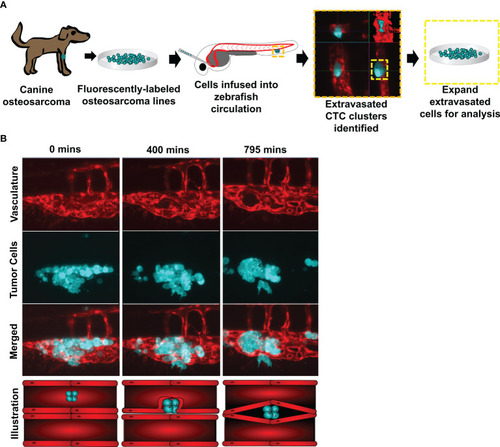
Figure 1 Circulating canine osteosarcoma clusters extravasate by angiopellosis. (A) Illustration of the project workflow. Canine osteosarcoma cell lines were fluorescently labeled and infused into the circulation of Tg(fli1a:egpf) with fluorescent blood vessels. Tumor cells which extravasated as clusters were isolated and expanded, and these sub-lines were then molecularly profiled. (B) Representative image of infused D17 tumor cells aggregating as clusters in zebrafish circulation. Tumor cell clusters begin to extravasate through the endothelial cells of the blood vessels during metastasis. The tumor cluster is eventually completely removed from the inside of the vessels and is lodged in an extravascular cavity while maintaining multicellularity and not disassociating into single cells. SB = 20µM. |
|
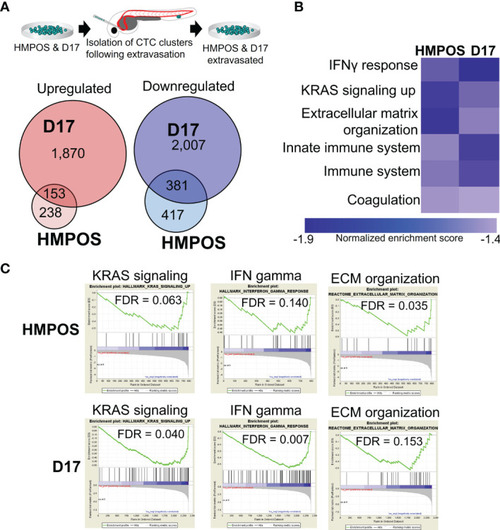
Extravasated circulating tumor cells display differential expression of genes and pathways. |
|
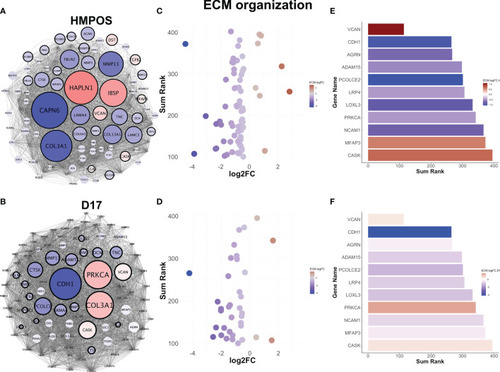
Extravasated circulating tumor cells downregulate extracellular matrix remodeling. |
|
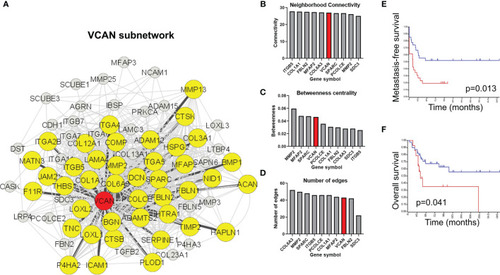
Versican-mediated extracellular matrix organization is enriched in extravasated circulating tumor cells. |
|
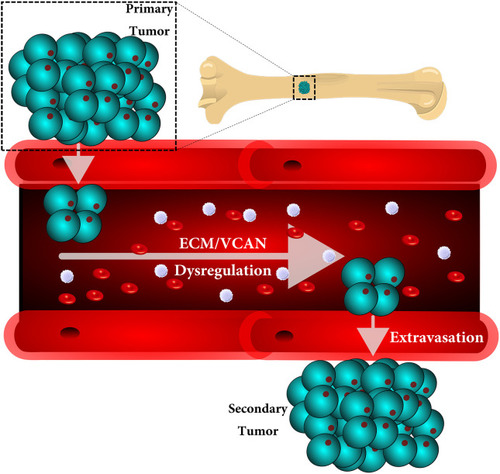
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT A graphical abstract of the proposed findings this study identified. |