- Title
-
Tools to Image Germplasm Dynamics During Early Zebrafish Development
- Authors
- Zaucker, A., Mitchell, C.A., Coker, H.L.E., Sampath, K.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
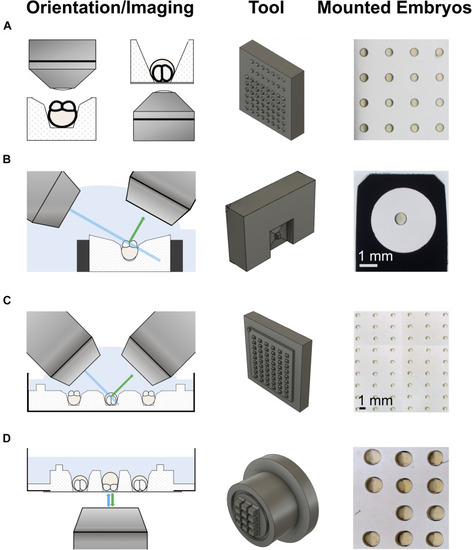
3d-printed tools for imaging on upright and inverted microscopes. The left column shows schematics of the different imaging modalities. The middle column shows the 3d-printed mounting tools. The right column shows examples of embryos mounted using the tools. |
|
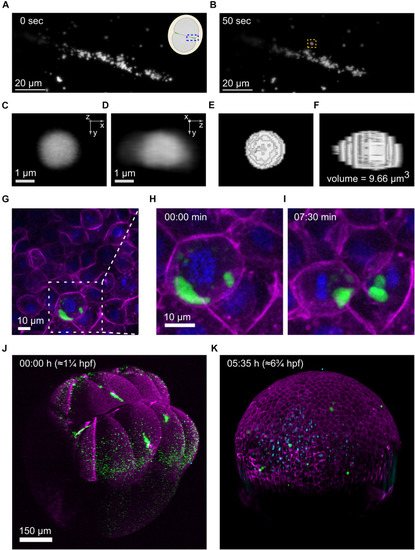
Imaging of germplasm across scales |