- Title
-
The RNA-binding protein Igf2bp3 is critical for embryonic and germline development in zebrafish
- Authors
- Vong, Y.H., Sivashanmugam, L., Leech, R., Zaucker, A., Jones, A., Sampath, K.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
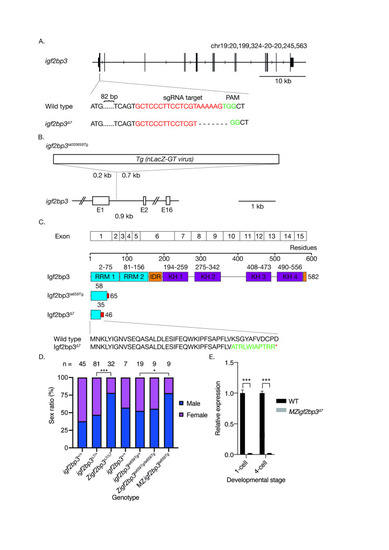
A. Generation of the |
|
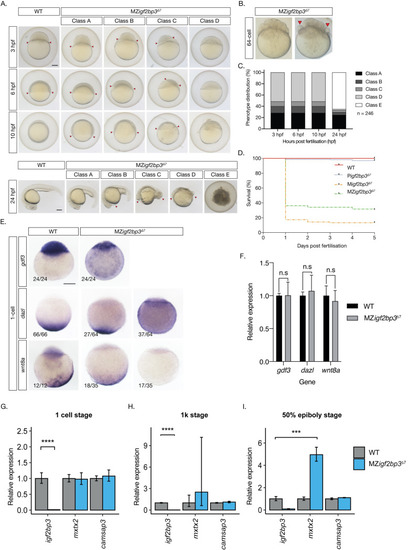
A. Maternal EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
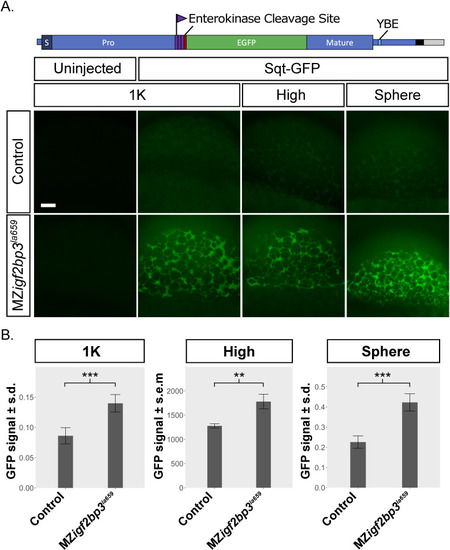
A. Schematic of the |
|
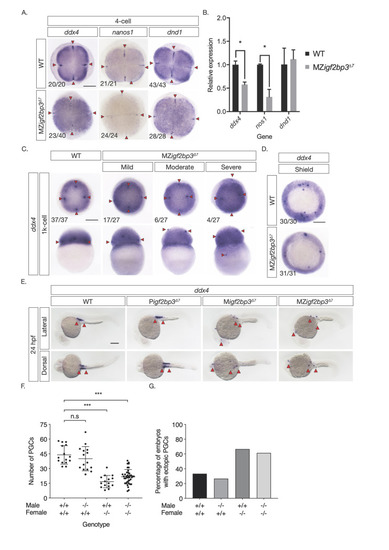
A. Whole mount in-situ hybridisation (WISH) in early embryos shows altered expression of germline markers ddx4, dnd1, and nanos1 in igf2bp3Δ7 mutant embryos. B. qRT-PCR to detect early germplasm markers shows reduced levels of ddx4 and nos1 expression in mutant embryos at the 4-cell stage, whereas expression levels of dnd1 is not significantly different from control wild type embryos. C. Primordial germ cells (PGCs; red arrowheads) in igf2bp3Δ7 embryos are ectopically located at the 1k-cell stage to varying extents ranging from mild or moderate to severe. D. Primordial germ cells are severely reduced or not detected in igf2bp3Δ7 mutants by gastrula stages. E,F. WISH (E) and quantitation (F) of ddx4-positive cells (red arrowheads) shows reduced and ectopic primordial germ cells in 24 hpf maternal igf2bp3Δ7 (Migf2bp3Δ7) and maternal-zygotic igf2bp3Δ7 mutants (MZigf2bp3Δ7) compared to WT siblings and paternal igf2bp3Δ7 (Pigf2bp3Δ7) mutants; p *<0.05, **<0.01, ***< 0.001. G. Loss of maternal igf2bp3 leads to some ectopic primordial germ cells across the trunk (red arrowheads) and occasionally in the hindbrain region. Bar graph shows the number of embryos with ectopic germ cells in WT, Pigf2bp3Δ7, Migf2bp3Δ7, and MZigf2bp3Δ7 mutants. Scale bar in A and C-E, 200 μm. N = 15 embryos each for WT, Pigf2bp3Δ7, and Migf2bp3Δ7 and 39 for MZigf2bp3Δ7 mutants. |
|
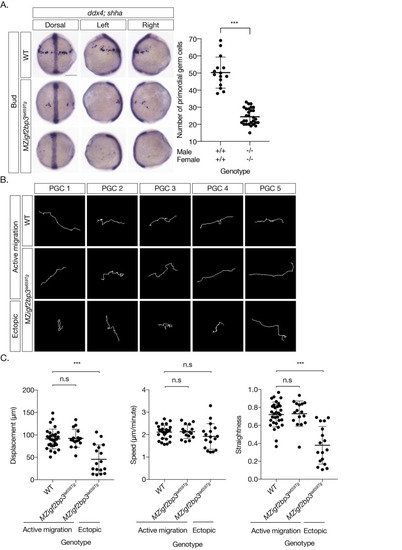
A. WISH to detect ddx4 positive PGCs and shh in the midline at Bud stage. PGCs are reduced (scatter plot, right) and ectopically located in MZigf2bp3la659Tg embryos compared to wild type (WT) embryos. B. Migration tracks of PGCs in bud stage embryos, labelled with GFP-nos1 reporter. MZigf2bp3la659Tg embryos show aberrant PGC migration compared to WT controls. C. PGC track analysis showing displacement, speed and straightness index. Ectopic PGCs in MZigf2bp3la659Tg mutants show significantly reduced total displacement and straightness, although speed of individual PGCs is not altered in mutant embryos compared to WT controls. Scale bars, 200 μm; p*<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001; Number of PGCs analysed = 31, 16 and 17 for WT, actively migrating and ectopic MZigf2bp3la659Tg PGCs, respectively. |
|
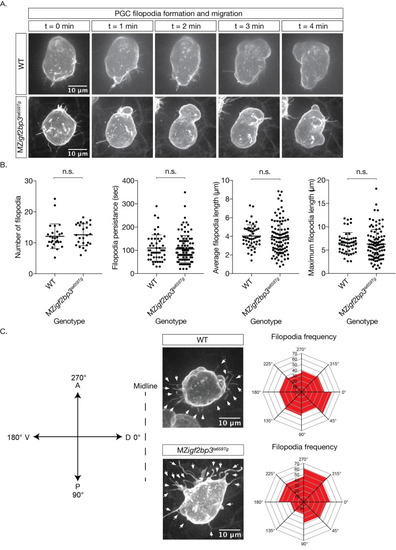
A. Images of cell membranes of PGCs labelled with a Farnesylated- |
|
A. Some PGCs are lost during migration in maternal |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |