- Title
-
The Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Ibrutinib Impairs the Vascular Development of Zebrafish Larvae
- Authors
- Wang, K., Xu, Q., Zhong, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Pharmacol
|
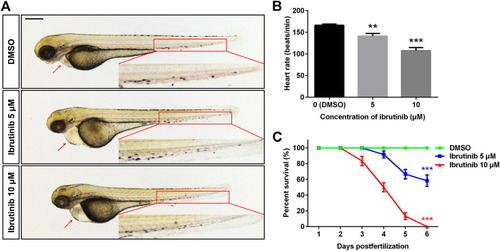
Ibrutinib had potent toxicity in zebrafish embryos. |
|
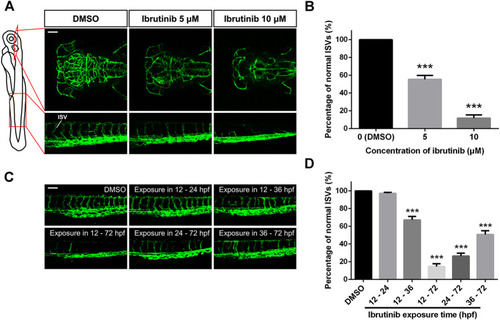
Vascular formation was perturbed in ibrutinib-treated embryos. |
|
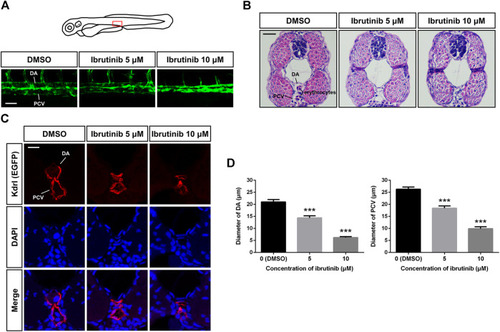
Vascular lumens were collapsed after ibrutinib treatment. |
|
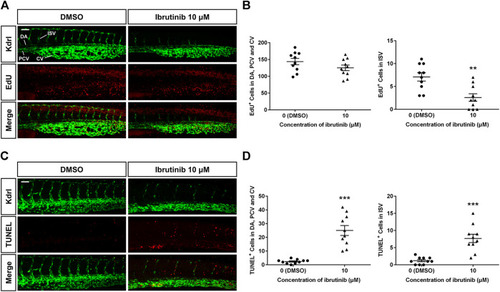
Reduced proliferation and enhanced apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) in ibrutinib-treated embryos. |
|
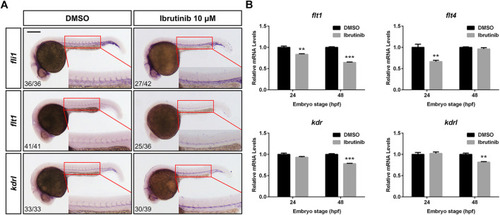
Ibrutinib exposure altered the expression of vascular development-related genes. (A) The expression pattern of vascular marker genes, fli1, flt1, and kdrl, was examined in ibrutinib-treated embryos by whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) at 24 h post-fertilization (hpf). Numbers at bottom left indicate the number of embryos with similar staining pattern among all embryos examined (Fisher’s exact tests, p < 0.001). (B) The qRT-PCR results showed the expression of VEGFR genes, flt1, flt4, kdr, and kdrl, in ibrutinib-treated embryos at 24 and 48 hpf. Asterisks indicate significant differences (DMSO vs. ibrutinib), **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. |