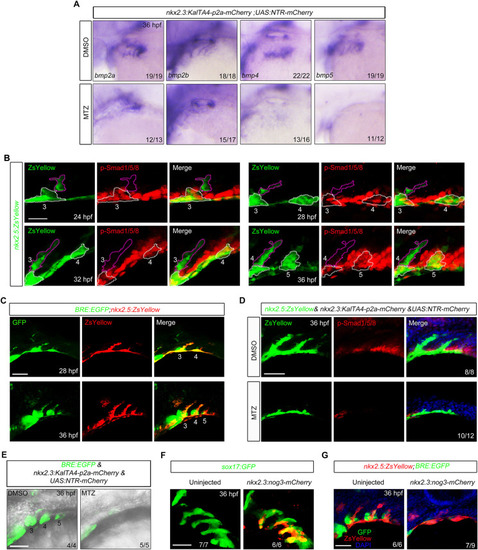
- Title
-
Pharyngeal pouches provide a niche microenvironment for arch artery progenitor specification
- Authors
- Mao, A., Zhang, M., Li, L., Liu, J., Ning, G., Cao, Y., Wang, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
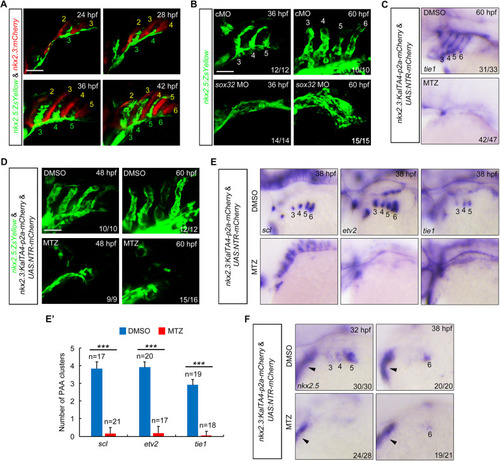
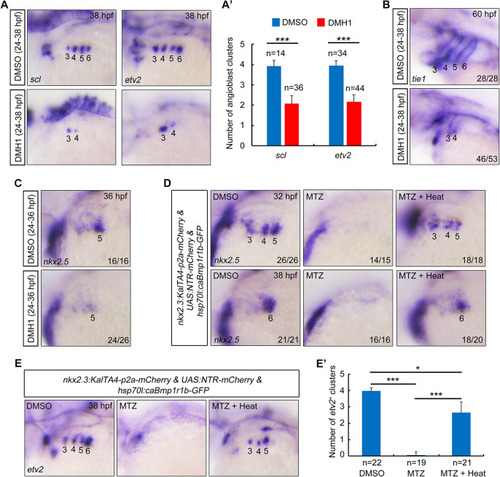
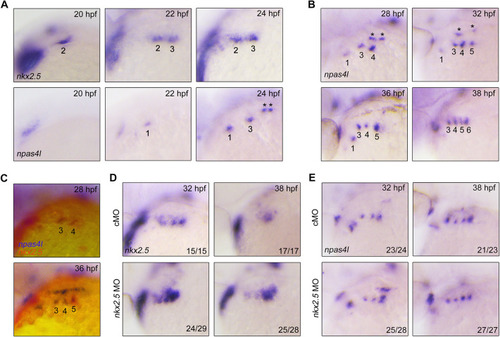
Inhibition of BMP signaling after PAA progenitor specification induces no detectable defects of PAA morphogenesis. (A) Live confocal images of Tg(nkx2.5:ZsYellow;gata1:DsRed) embryos with DMSO or 10 μM DMH1 treatment for different durations. White arrowheads indicate the new sprouting clusters after removal of DMH1 at 38 hpf. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Expression analysis of nkx2.5 by in situ hybridization in embryos subjected to different treatments. The dotted lines represent the area of expression of nkx2.5. Black arrowhead indicates the newly emerged expression of nkx2.5 after removal of DMH1. |
|
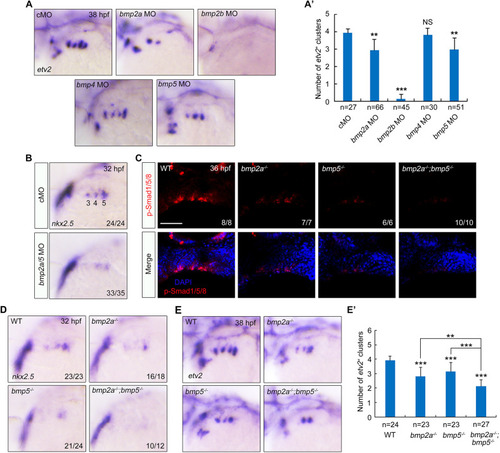
BMP2a together with BMP5 functions in PAA progenitor specification. (A,A′) The expression of etv2 in embryos injected with indicated MO was analyzed by in situ hybridization (A). Injection doses: bmp2a MO, 2 ng; bmp2b MO, 0.3 ng; bmp4 MO, 2 ng; bmp5 MO, 4 ng. The average numbers of etv2+ PAA angioblast clusters were quantified from three independent experiments, and the group values are expressed as mean±s.d. (A′). Student's t-test (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001; NS, no significant difference). (B) Knockdown of bmp2a and bmp5 disrupted the specification of PAA progenitors. Wild-type embryos were injected with bmp2a and bmp5 MOs at the one-cell stage. The resulting embryos were harvested for in situ hybridization. (C) Wild-type and indicated mutant embryos were harvested at 36 hpf for immunofluorescence assay with anti-p-Smas1/5/8 antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. There is a distinct decrease of p-Smad1/5/8 in the bmp2a−/−;bmp5−/− double mutants. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D-E′) Expression analysis of nkx2.5 (D) and etv2 (E) in bmp2a−/− or bmp5−/− embryos and bmp2a−/−;bmp5−/− double mutants by in situ hybridization. The average numbers of etv2+ angioblast clusters were quantified from three independent experiments and the group values were expressed as mean±s.d. (E′). Student's t-test was used to determine the significance of differences between wild-type animals and each mutant, and one-way ANOVA test was performed to analyze the statistical differences between bmp2a−/−;bmp5−/− double mutants and bmp2a−/− or bmp5−/− embryos. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. |
|
|
|
|