- Title
-
Zebrafish xenograft model of human lung cancer for studying the function of LINC00152 in cell proliferation and invasion
- Authors
- Shen, W., Pu, J., Sun, J., Tan, B., Wang, W., Wang, L., Cheng, J., Zuo, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Cancer Cell Int.
|
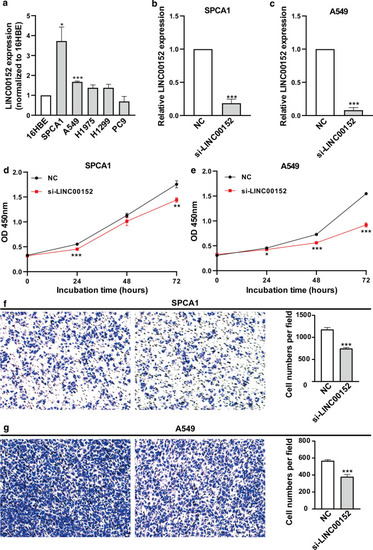
Knockdown of LINC00152 decreases the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells in vitro. |
|
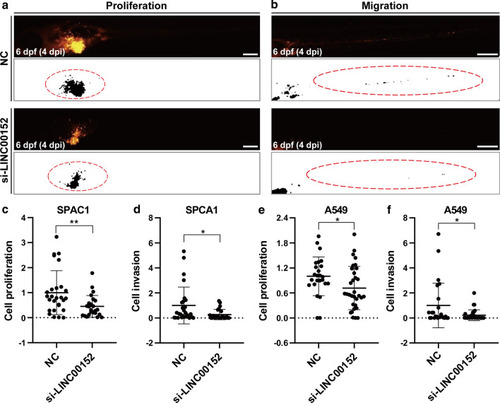
Knockdown of LINC00152 decreases the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells in zebrafish xenograft by stereomicroscopy. |
|
Knockdown LINC00152 decreases the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells in zebrafish xenograft by confocal microscopy. |
|
Knocking down LINC00152 and blocking EGFR have a synergic effect on the inhibition of cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. |
|
Knockdown of LINC00152 and block of EGFR have a synergic effect of inhibition in cell proliferation in zebrafish xenograft. |