- Title
-
Xanthotoxin reverses Parkinson's disease-like symptoms in zebrafish larvae and mice models: a comparative study
- Authors
- Kozioł, E., Skalicka-Woźniak, K., Michalak, A., Kaszubska, K., Budzyńska, B.
- Source
- Full text @ Pharmacol Rep
|
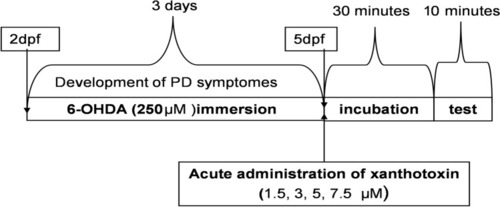
Diagram shows the schedule of administration of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) (immersion) and xanthotoxin (XT) in zebrafish Parkinson’s disease protocol ( |
|
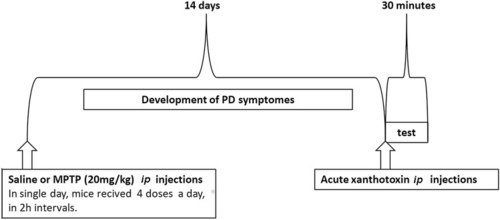
Diagram shows the schedule of administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP, ip) and xanthotoxin (XT) in mice Parkinson’s disease protocol ( |
|
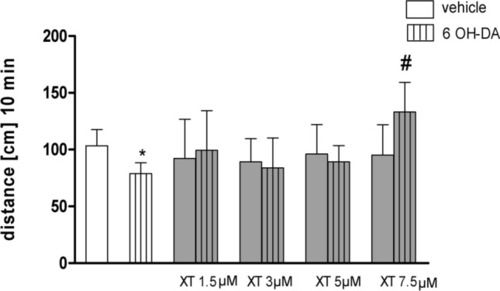
The effects of xanthotoxin (XT) on 6-hydroxydopamine(6-OHDA) induce locomotor impairments in zebrafish. Larvae were treated with E3 solution (vehicle) or 6-OHDA (250 µM, 4 days). 30 min before experiment larvae were incubated in different concentrations of XT (1.5, 3, 5, 7.5 µM). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM, * PHENOTYPE:
|
|
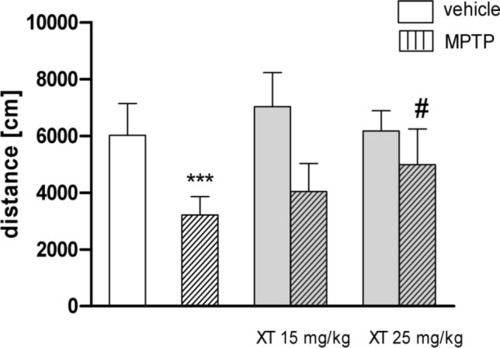
The effects of xanthotoxin (XT) on 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced locomotor impairments. Mice were injected with saline or MPTP (20 mg/kg, 4 doses a day, every 2 h). XT (15 and 25 mg/kg) was administered acutely, immediately before locomotor activity measurement 14 days after MPTP administration. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM, *** |