- Title
-
Phenotype-Based Screening of Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Dravet Syndrome Zebrafish Model
- Authors
- Griffin, A., Anvar, M., Hamling, K., Baraban, S.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Pharmacol
|
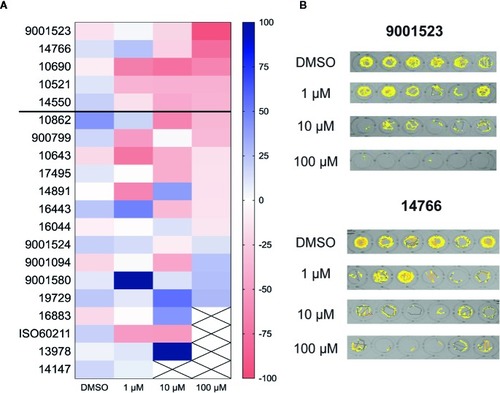
A library of synthetic cannabinoids (SCs) was screened for their ability to reduce the high velocity seizure-like swim behavior of 5 day old zebrafish larvae. Compounds were screened at |
|
Behavioral screening of 20 compounds which were identified as positive from the library screens. |
|
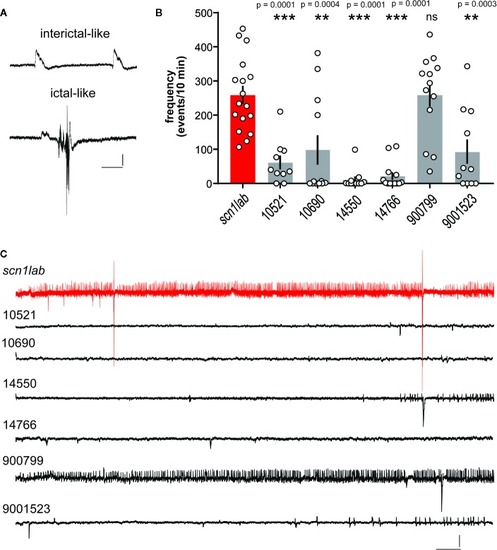
Electrophysiological assay for compounds identified in the locomotion-based screening assay. |
|
Structural comparison of SC identified to reduce spontaneous seizures in the |