- Title
-
Phage Lytic Protein LysRODI Prevents Staphylococcal Mastitis in Mice
- Authors
- Gutiérrez, D., Garrido, V., Fernández, L., Portilla, S., Rodríguez, A., Grilló, M.J., García, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Microbiol
|
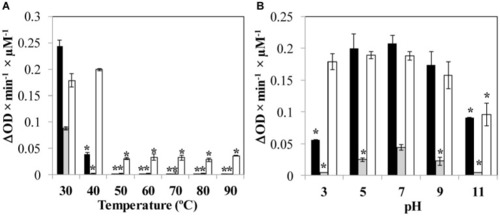
Influence of environmental parameters |
|
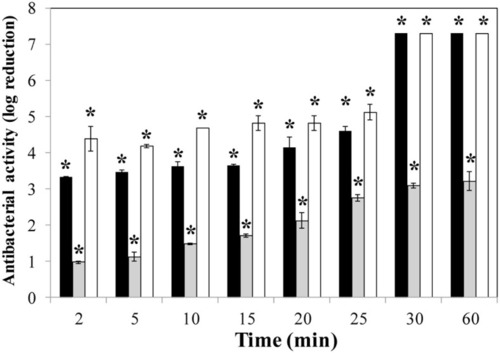
Time-kill curve of |
|
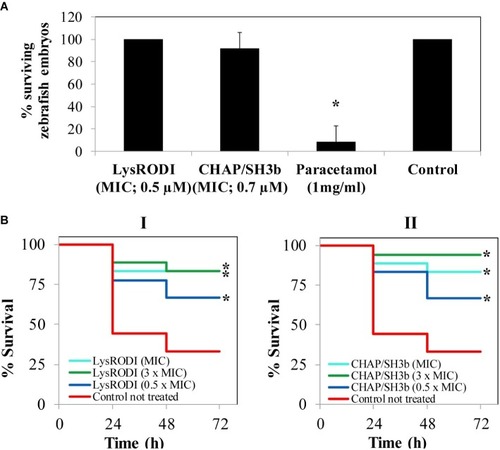
Evaluation of safety and activity of LysRODI and CHAPSH3b using a zebrafish model. |
|
Efficacy of LysRODI preventive treatment in a mastitis mouse model. CD1 lactating mice at breastfeeding day 10 were treated by intramammary administration of 24 μg of LysRODI and challenged 90 min later with 5 × 104 CFU/mice of |