- Title
-
A systems biology approach reveals neuronal and muscle developmental defects after chronic exposure to ionising radiation in zebrafish
- Authors
- Murat El Houdigui, S., Adam-Guillermin, C., Loro, G., Arcanjo, C., Frelon, S., Floriani, M., Dubourg, N., Baudelet, E., Audebert, S., Camoin, L., Armant, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
( |
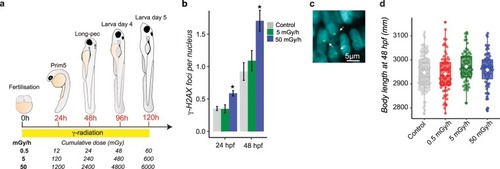
|
( |
|
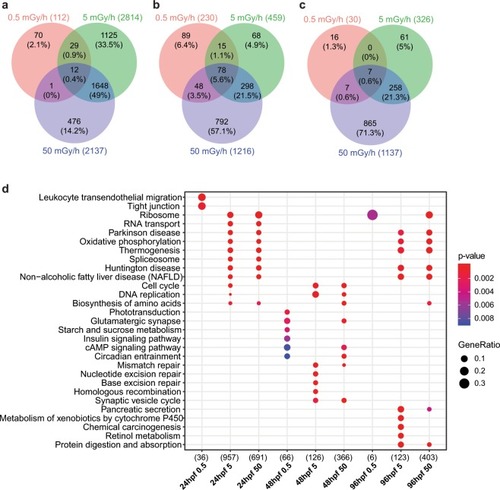
Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes at the three dose rates (|fold change| ≥ 1.5 and adjusted p-value < 0.01), at ( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
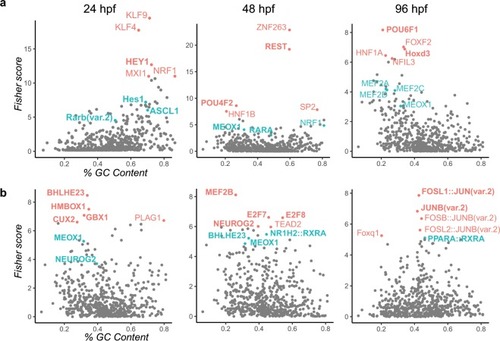
Volcano plots of deregulated proteins in 96 hpf larvae exposed ( |
|
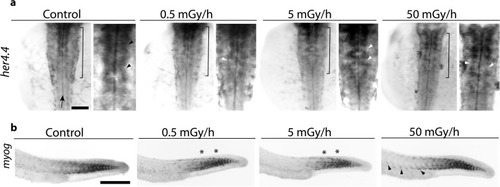
Whole mount RNA |
|
( |