- Title
-
Zebrafish TRIM25 Promotes Innate Immune Response to RGNNV Infection by Targeting 2CARD and RD Regions of RIG-I for K63-Linked Ubiquitination
- Authors
- Jin, Y., Jia, K., Zhang, W., Xiang, Y., Jia, P., Liu, W., Yi, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
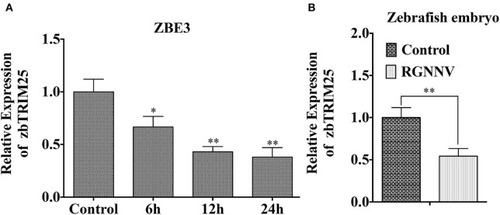
zbTRIM25 expression is inhibited in zebrafish during RGNNV infection. |
|
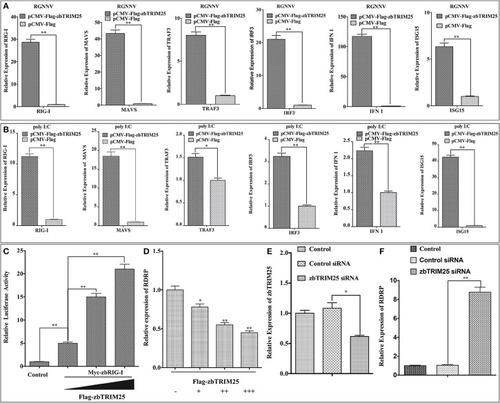
zbTRIM25 potentiates RLR signaling pathway. |
|
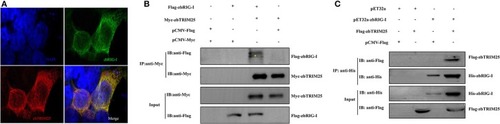
zbTRIM25 interacts with zbRIG-I. |
|
Physical interaction of zbTRIM25 with zbRIG-I. |
|
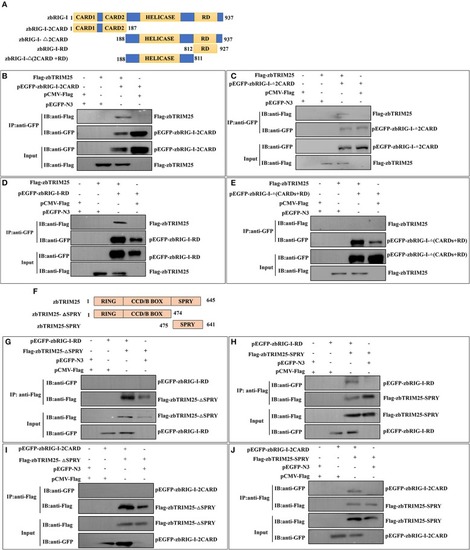
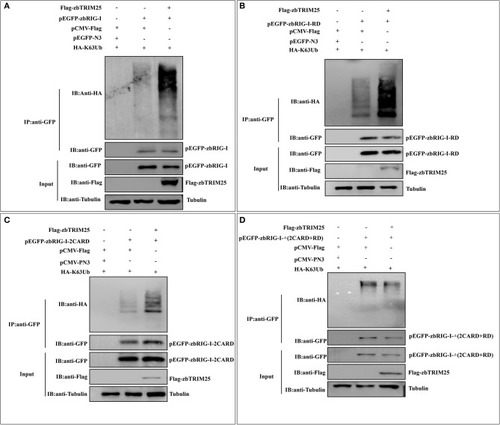
zbTRIM25 promotes zbRIG-I ubiquitination. |
|
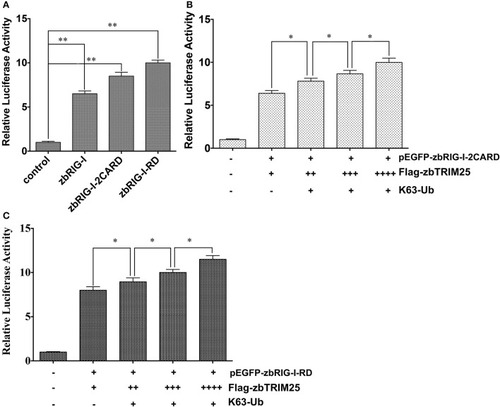
zbTRIM25-mediated K63 ubiquitination in 2CARD and RD regions of zbRIG-I is important for IFN induction. |
|
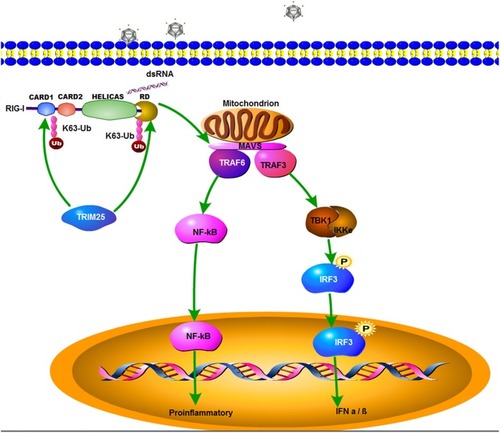
A schematic model of zbTRIM25-mediated RLR signaling pathway during RGNNV infection. zbTRIM25 interacts with and catalyzes the K63 polyubiquitination of 2CARD and RD regions of zbRIG-I, which subsequently induces the activation of downstream signaling event via MAVS, and thereby inhibits viral infection. |