- Title
-
Inhibition of Classical and Alternative Modes of Respiration in Candida albicans Leads to Cell Wall Remodeling and Increased Macrophage Recognition
- Authors
- Duvenage, L., Walker, L.A., Bojarczuk, A., Johnston, S.A., MacCallum, D.M., Munro, C.A., Gourlay, C.W.
- Source
- Full text @ MBio
|
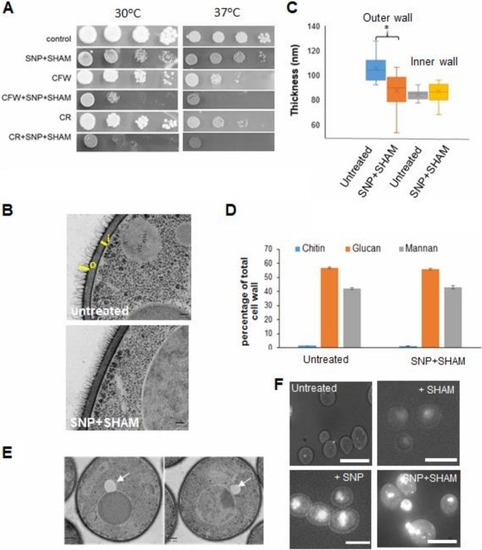
SNP+SHAM treatment leads to cell wall alterations and altered lipid metabolism. (A) Wild-type cells were serially diluted (1:10 dilutions), and equal volumes were spotted onto YPD plates (at 30 or 37°C) containing 1 mM SNP–0.5 mM SHAM and 25 µg/ml calcofluor white (CFW) or 40 µg/ml Congo red (CR). (B) Cells were treated with 1 mM SNP–0.5 mM SHAM for 18 h and processed for transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Representative examples of untreated and SNP+SHAM-treated cells are shown. Bar = 100 nm. (C) Quantification of outer cell wall (o) and inner cell wall (i) thicknesses was carried out from TEM images. Measurements were taken at 5 points along the cell wall for 25 cells per group. Bar = 100 nm. (D) Cell wall material was extracted and acid hydrolyzed from cells treated with 1 mM SNP–0.5 mM SHAM for 18 h, followed by HPLC analysis ( |
|
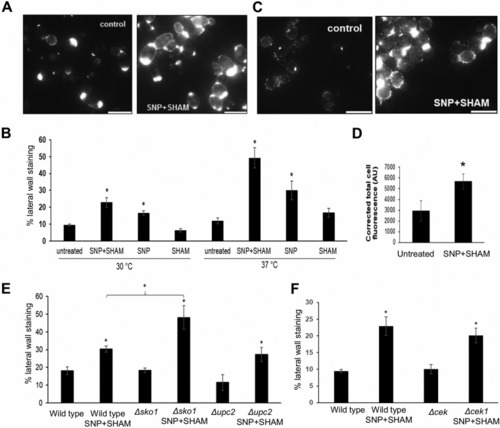
SNP+SHAM treatment induces surface exposure of chitin and β(1,3)-glucan. (A) Representative examples of untreated cells and cells treated with 1 mM SNP–0.5 mM SHAM for 18 h, stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), and analyzed using fluorescence microscopy. (B) Cells treated with SNP, SHAM, or SNP+SHAM at 30 or 37°C were quantified for FITC-WGA staining as described in Materials and Methods ( |
|
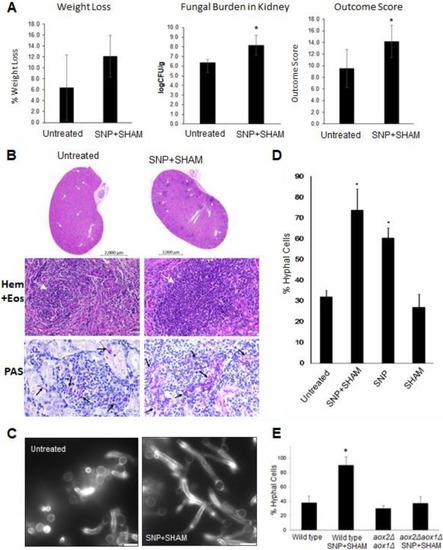
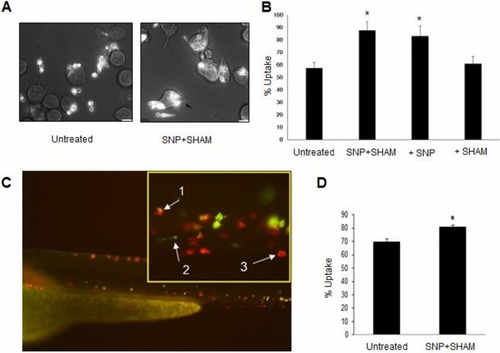
Pretreatment of |
|
PHENOTYPE:
|