- Title
-
'Central' Actions of Corticosteroid Signaling Suggested by Constitutive Knockout of Corticosteroid Receptors in Small Fish
- Authors
- Sakamoto, T., Sakamoto, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Nutrients
|
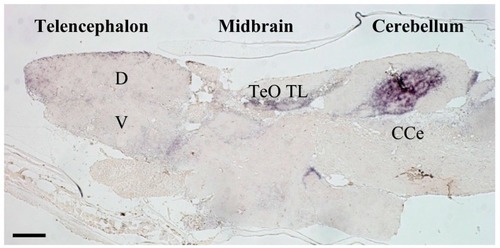
Photomicrograph of mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in-situ hybridization in medaka brain. MR expression is restricted to a number of important areas that likely correspond to homologous brain regions containing MR in other vertebrates including those of humans [ |