- Title
-
Novel NEK8 Mutations Cause Severe Syndromic Renal Cystic Dysplasia through YAP Dysregulation
- Authors
- Grampa, V., Delous, M., Zaidan, M., Odye, G., Thomas, S., Elkhartoufi, N., Filhol, E., Niel, O., Silbermann, F., Lebreton, C., Collardeau-Frachon, S., Rouvet, I., Alessandri, J.L., Devisme, L., Dieux-Coeslier, A., Cordier, M.P., Capri, Y., Khung-Savatovsky, S., Sigaudy, S., Salomon, R., Antignac, C., Gubler, M.C., Benmerah, A., Terzi, F., Attié-Bitach, T., Jeanpierre, C., Saunier, S.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
NEK8 overexpression in zebrafish induces Hippo pathway deregulation. (A) Representative pictures of the different classes of body phenotype observed upon nek8 morpholino (MO) or human NEK8-GFP RNA injections in zebrafish embryos. Arrowhead points out cyclopia observed in a subset of short embryos. (A') Graph showing the distribution of the three classes of body axis curvature observed in rescue experiments with WT or mutated (T87A, R602W) NEK8-GFP RNA forms. 30% of embryos co-injected with nek8 MO and WT NEK8-GFP RNA exhibited a stunted dorsally curved body axis similar to embryos injected with human YAP RNA. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 90 to 180 embryos). (A'') Graph showing the distribution of normal and stunted dorsally curved animals among GFP or WT NEK8-GFP RNA injected embryos upon Verteporfin (VP) treatment. A partial rescue of the phenotype can be observed in the presence of 20 μM Verteporfin. Data are from four independent experiments (n = 120 to 240 embryos). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
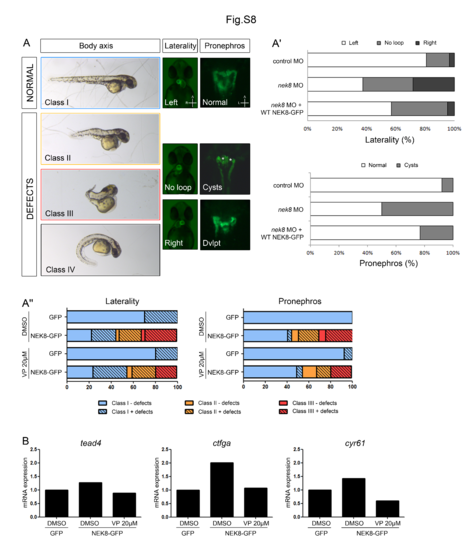
Verteporfin treatment partially rescues pronephric defects induced by NEK8 overexpression in zebrafish embryos. (A) Representative images of body axis, laterality (heart looping) and pronephros defects observed in zebrafish embryos. Four classes have been determined depending of the body shape, class I (blue) for normal embryos, class II (orange) for embryos with shortened axis, class III (red) for embryos with severely shortened and dorsally curved body axis, and class IV (black, only observed with nek8 MO) with ventrally curved body axis. Laterality defects encompass no looped and right-sided hearts compare to normal left-sided heart. Ventral views, anterior to the top. Pronephros defects encompass cystic glomeruli (asterisks) and developmental (Dvlpt) abnormalities. Dorsal views, anterior to the top. Tg(cmlc2:GFP) and Tg(wt1b:GFP) transgenic lines were used to observe heart looping and pronephros morphology, respectively. (A’) Graphs representing the proportions of embryos presenting laterality defects (top panel) and pronephric cysts (bottom panel) in control MO-, nek8 MO- and nek8 MO/human NEK8-GFP RNA-injected embryos. (A”) Graphs representing the proportions of embryos presenting laterality (left panel) and pronephros (right panel) defects (dashed bars) within each class of body axis shape, in control GFP and human NEK8-GFP RNA-injected embryos, treated with DMSO or Verteporfin (VP, 20 μM) from 90% epiboly to 34 hpf. (B) qPCR analysis of Yap target gene expression, tead4, ctgfa, cyr61, in human NEK8-GFP RNA-injected embryos treated with DMSO or Verteporfin (VP, 20 μM) compare to control GFP RNA injected embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|