- Title
-
Appendage expression driven by the Hoxd Global Control Region is an ancient gnathostome feature
- Authors
- Schneider, I., Aneas, I., Gehrke, A.R., Dahn, R.D., Nobrega, M.A., and Shubin, N.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
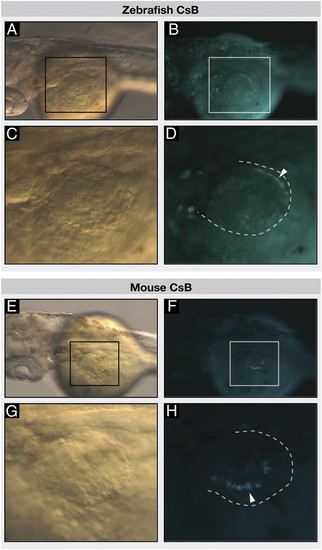
Vertebrate CsB enhancers drive neural tube and distal fin GFP expression in transgenic zebrafish. Transgenic zebrafish embryos injected with zebrafish CsB (A–D) or mouse CsB (E–H), at 52 hpf, anterior to the left. Dorsal view of zebrafish embryos; black and white boxes indicate position of the fin in bright field (A and E) and fluorescence (B and F), respectively. (C and G) Bright-field images show dorsal view of fins. (D and H) Dotted lines indicate position of fins, white arrowheads indicate eGFP signal in fins. |
|
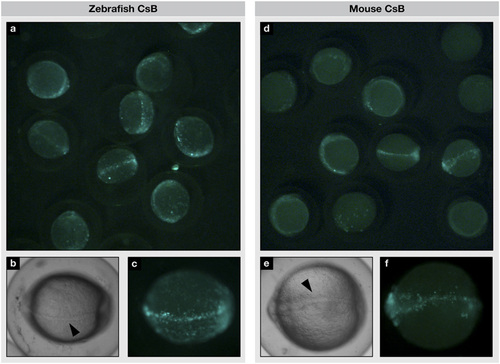
CsB enhancer activity in transgenic zebrafish during early development. Transgenic zebrafish embryos injected with zebrafish CsB (A–C) or mouse CsB (D–F), at 10 hours postfertilization (hpf). (A and D) Group photo of eGFP-positive zebrafish embryos. (B and E) Bright-field and (C and F) fluorescent images show eGFP signal along the midline. Black arrowheads denote notochord; anterior to the left. |
|
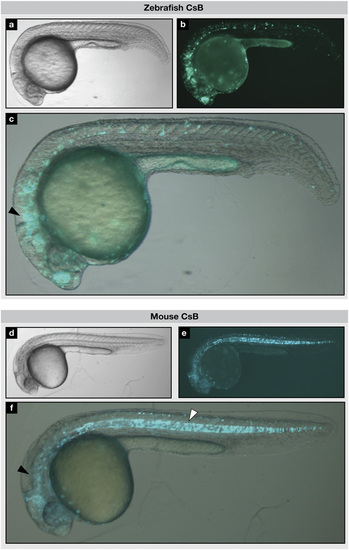
CsB enhancer activity in neural tube and notochord of transgenic zebrafish. Transgenic zebrafish embryos injected with zebrafish CsB (A–C) or mouse CsB (D–F), at 26 to 30 hpf. (A and D) Bright-field, (B and E) fluorescent, and (C and F) overlay images show eGFP signal in the brain, neural tube (black arrowheads) and notochord (white arrowhead). |