- Title
-
Identification of adult mineralized tissue zebrafish mutants
- Authors
- Andreeva, V., Connolly, M.H., Stewart-Swift, C., Fraher, D., Burt, J., Cardarelli, J., and Yelick, P.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Genesis
|
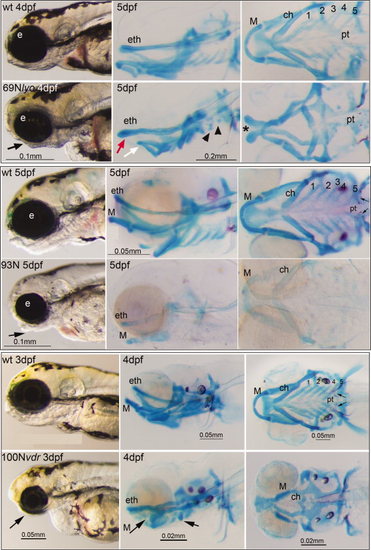
Early lethal craniofacial phenotypes. Examples of EL phenotypes are presented. For each, the left hand panels show lateral views of living embryos, middle panels show lateral views of Ab and Alizarin Red (Ab/AR)-stained larvae, and right hand panels show ventral views of Ab/AR-stained larvae. Small arrows point to pharyngeal teeth (pt). For the 69N Lyon mutant, the black arrow indicates a smaller lower jaw of 69N lyon (lyo), the red arrow indicates a rostrocaudally extended ethmoid plate, and the white arrow indicates a shortened Meckel′s cartilage. The black arrowheads point to rudimentary branchial arch cartilages of 69N lyo embryo, and an asterisk indicates the clefted ethmoid plate. The black arrow in the 93N mutant panel indicates aberrant shape of the lower jaw. The black arrows in the 100N mutant panel indicate a reduced lower jaw, Meckel′s cartilage, and ceratohyal cartilage element. Abbreviations: ch, ceratohyal; eth, ethmoid plate; e, eye; M, Meckel′s cartilage; pt, pharyngeal teeth; wt, wild type; ch, 1-5, branchial arches. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
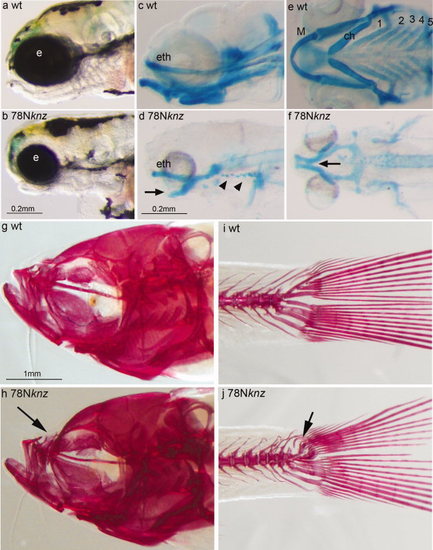
Homozygous and heterozygous phenotypes of the 78N knjaz (knz) mutant. (a, b) Lateral view of live 4 dpf wt (a) and 78N knjaz (knz) mutant (b) larvae. (c–f) Lateral (c, d) and (e, f) views of Ab/AR-stained 4 dpf wt (c, e) and 78N knjaz (knz) mutant (e, f) embryos. Arrows in (d) and (f) indicate Meckel′s cartilage, and arrowheads in (d) indicate missing branchial arche cartilages. (g–j) Lateral view of AR stained of adult wt (g, i) and 78N knjaz (knz) mutant (h, j) zebrafish. Arrow in (h) points to altered upper jaw morphology in knz mutants. Arrow in (j) points to defects in pleurostyle and hypural bones of knz mutant. Abbreviations: ch, ceratohyal; eth, ethmoid plate; e, eye; M, Meckel′s cartalige; wt, wild type; 1-5, branchial arches. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
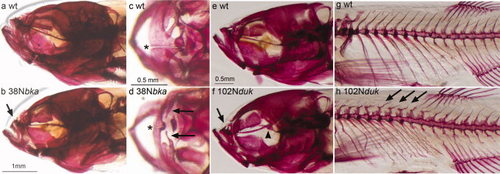
Adult craniofacial phenotypes of the 38N belka (bka) and 102N dushka (duk) mutants. (a–h) Alizarin red (AR)-stained adult zebrafish. (a,b,e,f) Lateral views of heads of wt (a,e), and 38N bka (b) and 102N duk (f) mutant siblings. The arrows in (b) and (f) point to reduced upper jaw in both mutants. The arrowhead in (f) points to bent parasphenoid in 102N duk mutant. (c,d) Dorsal view of upper jaw in wt (c) and 38N bka mutant (d) siblings. The asterisks indicate patent suture in wt maxilla (c), and fused suture in 38N bka mutant maxilla (d). Arrows in (d) indicate small maxillary bones in 38N bka mutants. (g,h) Lateral view of axial skeleton in wt (g) and 102N duk mutant (h) siblings. Arrows indicate small and misshapen neural arch cartilages in 102N duk mutants. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
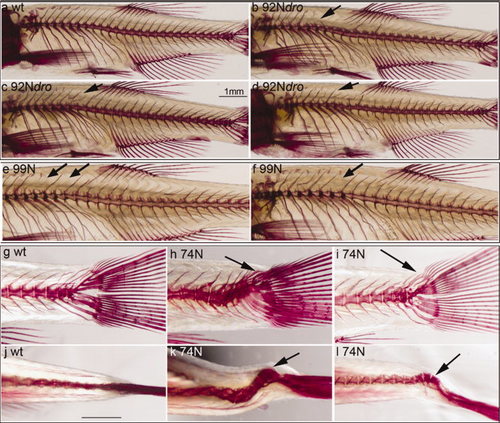
Adult skeletal phenotypes of 74N, 92N droog (dro), and 99N mutants. Lateral views of wt AR-stained axial skeleton (a). Lateral view of AR-stained axial skeletons of 92N dro(b-d) and 99N (e,f) mutants. Arrows in (b-f) point to missing neural arches. (g) Lateral view of AR-stained wt (g), and 74N mutant (h,i) tails. Arrows point to misshaped tail structures in 74N mutant. Dorsal view of AR-stained wt (j) and 74N mutant (k, l) tails. Arrows point to scoliosis in 74N mutant tails. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|