- Title
-
Characterization of the internal IRES element of the zebrafish connexin55.5 reveals functional implication of the polypyrimidine tract binding protein
- Authors
- Ul-Hussain, M., Dermietzel, R., and Zoidl, G.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Mol. Biol.
|
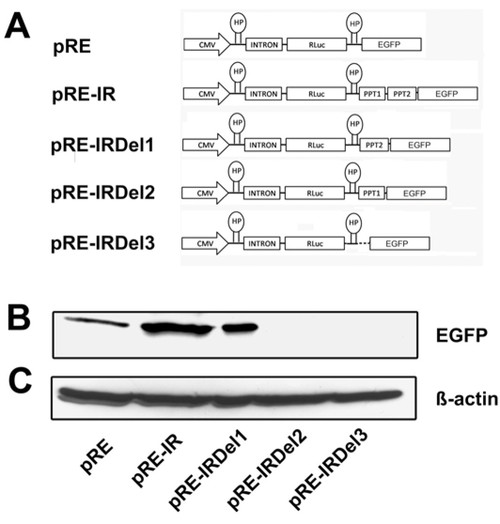
Western blot of wild type IRES element and its deletion mutants substantiate the efficiency of the PTB elements: A) Schematic representation of Di-cis constructs used for the Western blot analysis. pRE; control vector having RLuc as first cistron and EGFP as downstream cistron, pRE-IR; wild type IRES containing Di-cis construct, pRE-IRDel1; PPT1 deleted, pRE-IRDel2; PPT2 deleted and pRE-IRDel3; PPT1 and PPT2 deleted IRES construct. B) Western blot of the constructs transiently transfected into N2A cells. 30 μg of cytosolic total proteins were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE. Immunodetection was done using anti-GFP (1:2000) as primary antibody and peroxidase labeled anti-mouse IgG (1:7,500) as secondary antibody. C) The detection of β-actin served as internal loading control. |
|
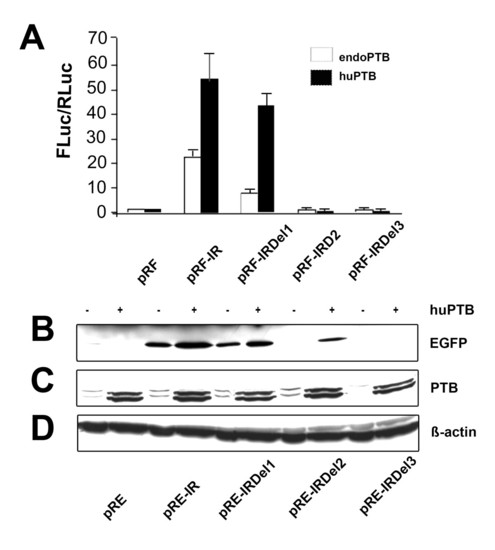
Overexpression of PTB enhances IRES activity: A) IRES activity of Di-cis constructs (see Fig. 1B) transiently transfected into N2A cells either in the presence of endogenous PTB or overexpressed human PTB (huPTB) by co-transfection with the pC1-PTB construct. IRES activity is represented as the ratio of Firefly to Rennila luciferase (FLuc/RLuc), with the activity of control vector pRF set to "1". Each construct was tested 4 times and each experiment was done in triplicates. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. B) Western blot of Di-cis constructs as summarized in Fig. 2A. All constructs were transiently transfected into N2A cells in the presence of either endogenous PTB (-) or over-expressed huPTB (+). 30 μg of total cytosolic proteins were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunodetection was done using anti-GFP (1:2,000) as primary antibody and peroxidase labeled anti-mouse IgG (1:7,500) as secondary antibody. C) Western blot of endogenous PTB and over-expressed huPTB from transiently transfected N2A cells. Immunodetection was done by using anti-PTB (1:1,000; Invitrogen) as primary antibody and peroxidase labeled anti-mouse IgG (1:7,500, Jackson ImmunoResearch) as secondary antibody. Note: endogenous and over-expressed huPTB is detected as a doublet band. D) Western blots applying β-actin served as loading control. |
|
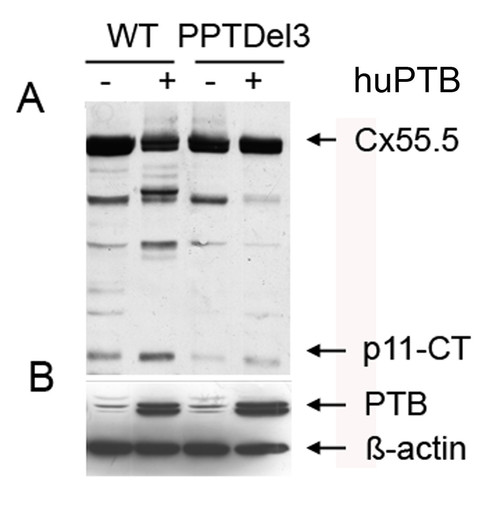
Polypyrimidine tracts and polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) regulate the expression of p11-CT. A) Western blot of wild type Cx55.5-EGFP (WT) and PPT1 and PPT2 deleted (WT-PPTDel3) fusion constructs transiently transfected in N2A cells in the presence of either endogenous PTB (-) or overexpressed PTB (+). Immunodetection was performed by using anti-GFP antibody as described above. B) Western blot detection of endogenous and huPTB using anti-PTB antibody as described above and with β-actin as loading control. |
|
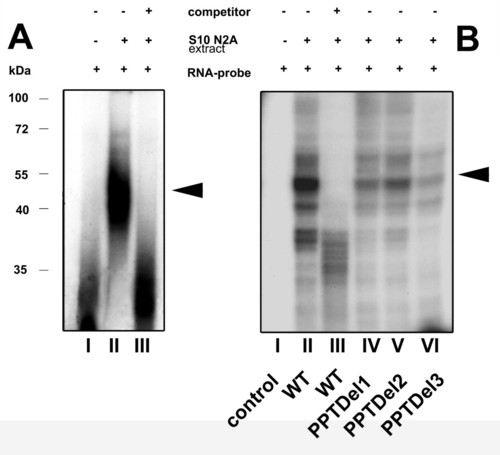
RNA-EMSA reveals a RNA-protein complex on the IRES element: A) RNA-EMSA of wild type IRES. Internally labeled 32P RNA-probes were incubated with S10 extract from N2A cells. RNA-protein complexes, resolved on a 4% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel were visualized by autoradiography. The presence of competitor (50 fold molar excess), S10 N2A extract and radiolabeled RNA probe is indicated by (+/-). The position of the RNA-protein binding complex is indicated by the arrow. B) UV cross-linking of RNA probes with S10 N2A extract: RNA-protein complexes were formed as indicated in (A) and samples were subjected to UV cross-linking followed by subsequent RNase treatment and resolved by 10% SDS PAGE. The composition of each sample is indicated as shown in A). Triangles on the right represent specific RNA-protein complexes and the numbers on the left represent a protein molecular weight marker kDa. Densitometrical analysis revealed a reduction to 39% (lane IV), 47% (lane V) and 27% (lane VI) with the wild type condition (lane II) set to 100%. |
|
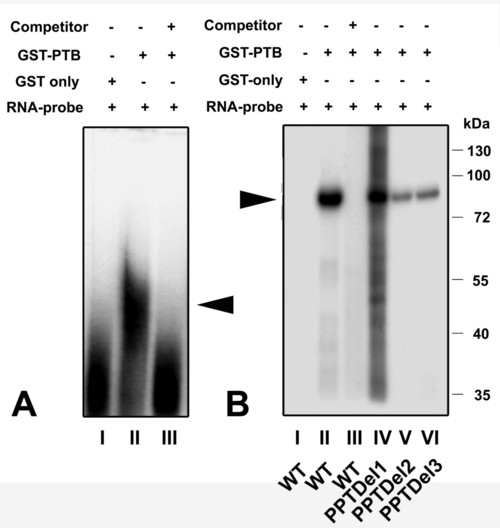
Recombinant GST-PTB fusion is able to bind the IRES element: A) RNA-EMSA of wild type 32P labeled IRES RNA with: lane I) ∼50 μg of purified GST only, lane II) 0.3 μg of purified GST/PTB fusion protein and lane III) cold competition of RNA-protein complex formed in (II) by 20 fold molar excess of unlabeled RNA. The triangle indicates the position of the RNA-protein complex. B) UV cross-linking of GST-PTB to the IRES element. Lane I) GST plus wild type IRES element. Lane II) GST-PTB fusion protein plus wild type IRES element. Lane III) cold competition of (II) using 50 fold molar excess of unlabeled RNA. Lane IV) PPTDel1, lane V) PPTDel2 and lane VI) PPTDel3 IRES mutants. A RNA-protein complex of about 84 kDa was detected in all cases (see triangle), but significantly less in PPTDel2 and PPTDel3 deletion mutants. This complex corresponds to a fusion protein of PTB (57 kDa) and GST (27 kDa). Numbers on right site represent a protein molecular weight marker in kDa. |
|
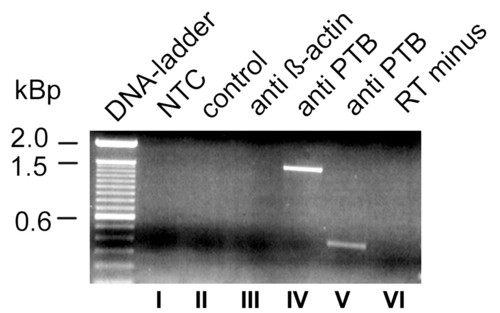
PTB antibodies precipitate Cx55,5 mRNA from transiently transfected N2A cells: Binding of PTB to Cx55.5 in living cells was tested 36 hrs post transfection. Crosslinked cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitate Cx55.5 RNAs using anti-PTB or anti-β-actin antibodies. RNAs binding to the antibody captured proteins were heat released, reversed transcribed and PCR amplified using primers specific for the Cx55.5 coding region. Lane I) NTC, no template control, lane II) control, PCR of cDNA reactions obtained from the samples immunoprecipitated with Protein A sepharose beads only (without any antibody), III) PCR reaction of cDNA obtained from the RNA immunoprecipitated from anti β-actin coated beads, IV) PCR of cDNA obtained from RNA reverse transcribed with primer pairs specific for the entire coding region (1497). V) cDNA from RNA reverse transcribed with nested primers for the carboxy-terminus fragment (400 bp). VI) RT-minus sample; RNA immunoprecipitated with PTB antibodies without reverse transcription. |