- Title
-
Duplication and Diversification of the Hypoxia-Inducible IGFBP-1 Gene in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Kamei, H., Lu, L., Jiao, S., Li, Y., Gyrup, C., Laursen, L.S., Oxvig, C., Zhou, J., and Duan, C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
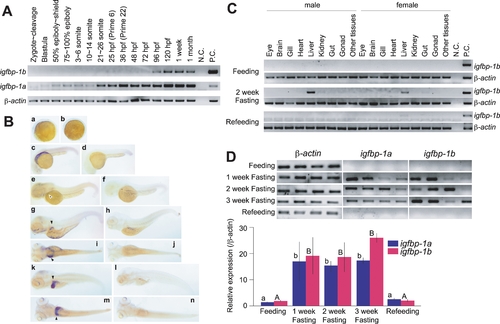
Temporal and spatial expression patterns of igfbp-1a and igfbp-1b during zebrafish embryogenesis. |
|
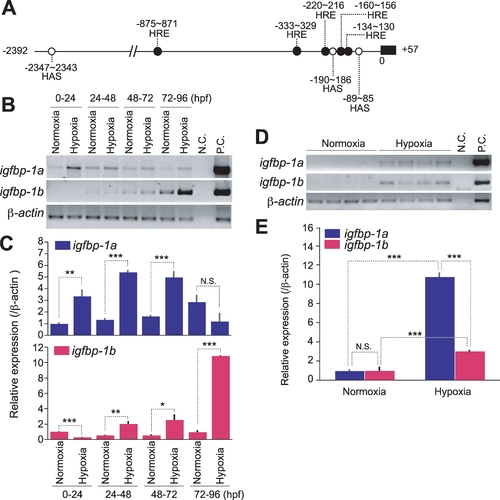
The expression levels of igfbp-1a and igfbp-1b are differentially regulated by hypoxia. |
|
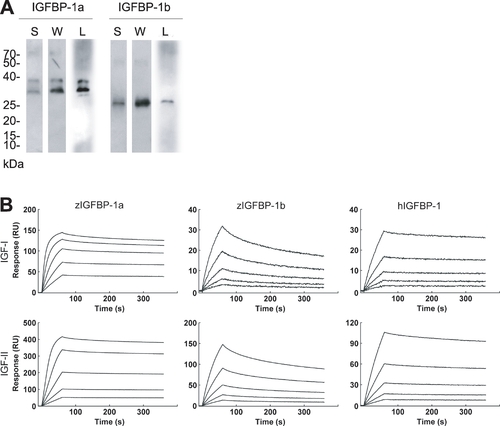
Zebrafish IGFBP-1a and -1b proteins have different IGF binding affinities and kinetics. |
|
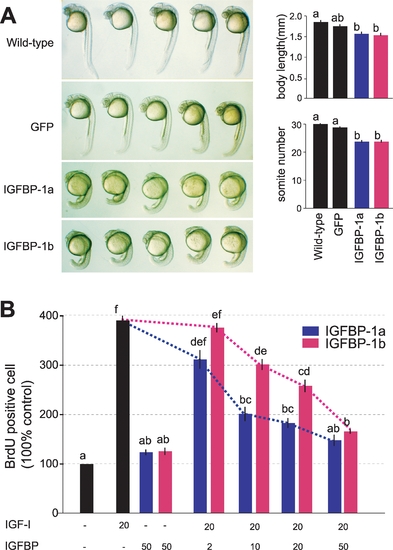
Zebrafish IGFBP-1a and IGFBP-1b are both functional but have different activities. |