- Title
-
The endocannabinoid receptor, CB1, is required for normal axonal growth and fasciculation
- Authors
- Watson, S., Chambers, D., Hobbs, C., Doherty, P., and Graham, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.
|
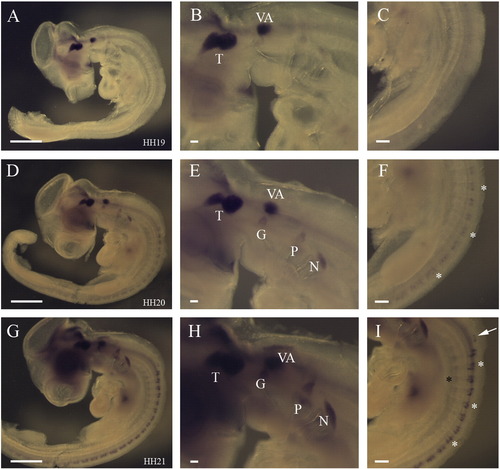
Establishment of CB1 expression in the peripheral nervous system. (A) Side view of a stage 19 whole embryos showing expression of CB1 in only the trigeminal and vestibuloaccoustic ganglia. (B) Higher power view of the head and (C) of the trunk. (D) Side view of a stage 20 embryo indicating that expression was additionally found in the geniculate, petrosal and nodose at this stage and had initiated in the dorsal root ganglia. (E) Higher power view of a stage 20 head showing expression in the cranial ganglia. (F) Higher power view of the trunk at stage 20 showing expression in the DRGs. (G) Side view of a stage 21 embryo, showing expression in the cranial sensory ganglia, the DRGs and the forming sympathetic ganglia. (H) Higher power view showing expression in the cranial ganglia. (I) Higher power view of the trunk highlighting the more pronounced expression in the DRGs and sympathetic ganglia had become apparent in the sympathetic ganglia. White asterisks highlight the positions of the DRGs, the black asterisk the position of the sympathetic chain. Abbreviations: T—trigeminal, VA—vestibuloaccoustic, G—geniculate, P—petrosal, N—nodose, DRGs—dorsal root ganglia. |
|
Maturation of CB1 expression in the spinal cord. (A–C) Sections of the spinal cord at the forelimb levels at stage 20. (A) Isl1 is expressed in the forming motor neurons and in the condensing DRGs. (B) Lack of CB1 expression. (C) Hu immunoreactivity in the mature motor neurons. (D–F) Sections of the spinal cord at forelimb level at stage 25. (D) Isl1 expression in the motor neurons, dorsal interneurons, DRGs and sympathetic ganglia. (E) CB1 expression in interneurons and DRGs and sympathetic ganglia. (F) Hu immunohistochemistry labels many neuronal populations in the spinal cord, and also the DRGs and sympathetics. (G–I) Sections of the spinal cord at the forelimb level at stage 29. (G) Isl1 is expressed by motor neurons, DRGs and sympathetic ganglia. (H) CB1 is expressed in many neuronal populations in the spinal cord and also in the DRGs. (I) Hu immunoreactivity labels many neurons in the spinal cord and the DRG. * indicates the position of the DRGs, MN—motor neurons, S—sympathetic ganglia. |
|
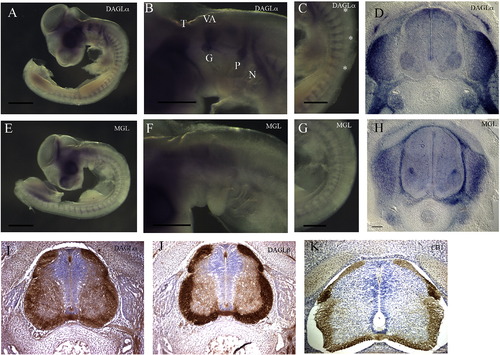
Analysis of the expression of the enzymes involved in the synthesis and catabolism of 2-AG. (A–D) Expression of DAGLα. (A) Side view of a stage 20 whole embryos showing expression of DAGLα in the cranial ganglia and spinal nerves. (B) Higher power view of the head showing expression in the developing cranial ganglia. (C) Higher power view of the trunk showing expression in the spinal nerves. (D) Section through the spinal cord at the forelimb level at stage 29, showing broad expression in the nerve cord, and expression in the DRGs and sympathetic ganglia. (E–H) Expression of MGL. (E) Side view of a stage 20 whole embryo hybridised for MGL. (F) Higher power view of the head. (G) Higher power view of the trunk. (H) Section through the spinal cord at the forelimb level at stage 29, showing broad expression in the nerve cord, at high levels in one group of interneurons, expression in the surrounding vasculature, and in the DRGs and sympathetic ganglia. (I–K) Sections through the spinal cord on an E6 chick stained with anti-DAGLα (I), anti-DAGLβ (J) and CB1 (K) antisera. |
|
Inhibiting CB1 function in chick embryo explants affects axonal growth. (A) Control explant cultured in DMSO. (B) Treated explant cultured in AM251. White arrows indicate MTN axons that have turned back on themselves. Abbreviations: MTN—mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus, R2—rhombomere 2, Tg—trigeminal ganglion. |
|
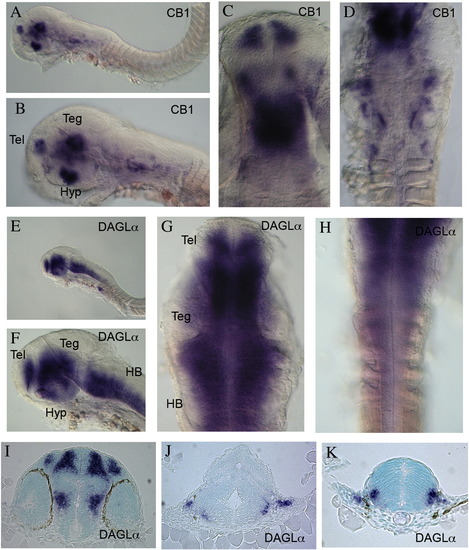
Expression of CB1 and DAGLα in zebrafish embryos. (A–D) Expression of CB1 in long pec stage, 48 hpf, embryos. (A) Overview of expression at this stage. (B) Higher power view showing expression in the head region. (C) High power dorsal view of the forebrain and midbrain. (D) High power dorsal view of the midbrain and hindbrain. (E–H) Expression of DAGLα in long pec stage, 48 hpf, embryos. (E) Overview of expression at this stage. (F) Higher power view showing expression in the head region. (G) High power dorsal view of the forebrain and midbrain. (H) High power dorsal view of the hindbrain and anterior spinal cord. (I) Section through the forebrain. (J) Section through the anterior hindbrain. (K) Section through the posterior hindbrain. Abbreviations: Teg—tegmentum, Tel—telencephalon, Hyp—Hypothalamus, HB—hindbrain. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
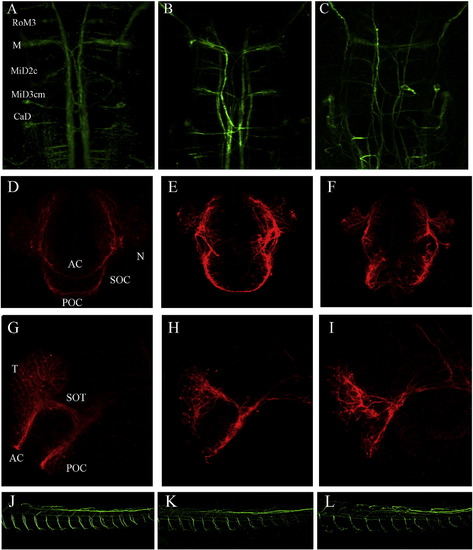
CB1 is required for the axonal outgrowth and fasciculation. (A–C) Neurofilament immunofluorescence of the hindbrain of zebrafish embryos, 72 hpf. (A) Control. (B) MO1 injected embryo (C) MO2 injected embryo. (D–I) Acetylated tubulin immunofluorescence of the anterior forebrain of zebrafish embryos, at prim 12. (D–F) Frontal views. (D) Control. (E) MO1 injected embryo. (F) MO2 injected embryo. (G–I) Side views. (G) Control. (H) MO1 injected embryo (I) MO2 injected embryo. (J–L) Side views of the trunk regions of 48 hpf zebrafish embryos stained with anti-neurofilament antibody (J) Control. (K) MO1 injected embryo. (L) MO2 injected embryo. Abbreviations: AC—anterior commissure, POC—posterior commissure, SOC—Supraoptic commissure, N—neurons. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 38(1), Watson, S., Chambers, D., Hobbs, C., Doherty, P., and Graham, A., The endocannabinoid receptor, CB1, is required for normal axonal growth and fasciculation, 89-97, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.