- Title
-
Molecular evolution and expression of zebrafish St8SiaIII, an alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase involved in myotome development
- Authors
- Bentrop, J., Marx, M., Schattschneider, S., Rivera-Milla, E., and Bastmeyer, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
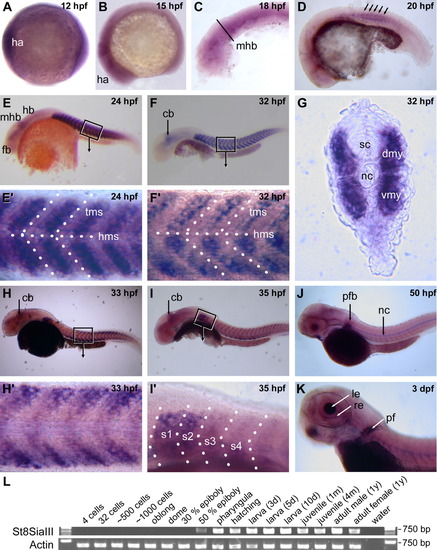
Expression of St8SiaIII during zebrafish development. A-K: In situ hybridizations using a St8SiaIII antisense probe. From 12 hpf to 15 hpf, St8SiaIII is expressed uniformly throughout the head anlage (A,B). Expression in the anterior nervous system is reduced to the midbrain hindbrain boundary around 20 hpf (C-E) and later to the cerebellum (F,H,I). As development proceeds, expression in the nervous system ceases, it is restricted to the retina and lens of the developing eye at 3 dpf (K). St8SiaIII expression in the somites starts at 20 hpf (D, arrows indicate first somites), peaks at 24 hpf (E, E′) and is down-regulated thereafter (F,F′, H,H′, I,I′). Down-regulation starts in the central parts of the somites (H′) and proceeds in an anterior-to-posterior fashion (H,I). At its peak expression, St8SiaIII is expressed uniformly throughout the fast muscle fibres of the entire myotome (G). St8SiaIII expression persists in somites 1 and 2 (I′) and is later found in the pectoral fins (J,K). Embryos in (A-F, H-K) are lateral views with rostral to the left and dorsal up; G shows a cross-section. Boxes in E, F, H, I indicate the regions shown in higher magnification in E′, F′, H′, I′, respectively. cb, cerebellum; dmy, dorsal myotome; fb, forebrain; ha, head anlage; hb, hindbrain; hms, horizontal myoseptum; le, lens; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; nc, notochord; pf, pectoral fin; re, retinal, s1-s4, somites 1-4; sc, spinal cord; tms, transversal myoseptum; vmy; ventral myotome. (L) reverse transcriptase PCR analysis of St8SiaIII transcripts in embryos, larvae, and adult zebrafish. St8SiaIII products were amplified with primers SiaIIIGSP3for and SiaIIIGSP3rev; controls show RT-PCR amplification of actin cDNA (Marx et al., 2007). St8SiaIII is expressed from 50% epiboly on throughout all developmental stages into adulthood. |
|
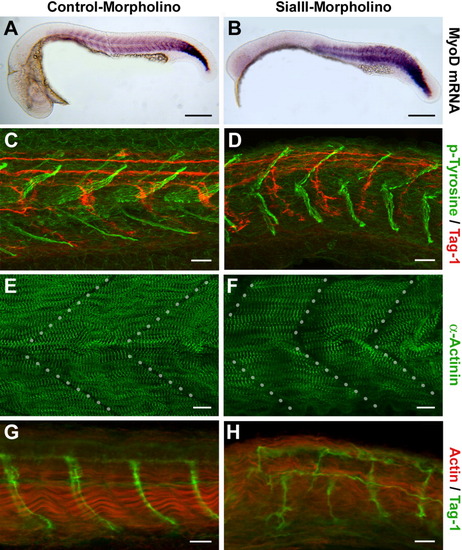
Knockdown of St8SiaIII induces malformations of myotomes and an abnormal growth pattern of motoneurons in developing zebrafish. A,C,E,G: Embryos injected with control morpholinos: (A, C, E) GeneTools control morpholino, (G) PST-morpholino (Marx et al., 2007). B,D,F,H: Embryos injected with St8SiaIII-specific morpholino (2 ng/μl). All embryos are shown rostral to the left. A, B: In situ hybridization using a mytome-specific probe (MyoD) shows a reduction of brain structures in morpholino-injected embryos at 25 hpf. C-F: Embryos at 33 hpf after morpholino knockdown immunolabelled for (C, D) phospho-Tyrosine (green) and the axonal marker Tag-1 (red) or (E, F) α-Actinin (green). Dotted lines in E and F indicate the transversal mysepta. Morphants are characterized by shortened myotomes and myosepta forming a more obtuse angle than in the controls. G,H: Embryos at 35 hpf after morpholino knockdown were immunolabelled for Actin (red) and the axonal marker Tag-1 (green). Muscle fibrils lose their well-ordered bundling, and motoraxons grow in a disordered pattern. Scale bars = 200 μm (A, B), 20 μm (C, D, G, H), 10 μm (E, F). |