- Title
-
Characterization of the enigma family in zebrafish
- Authors
- Ott, E.B., Sakalis, P.A., Marques, I.J., and Bagowski, C.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
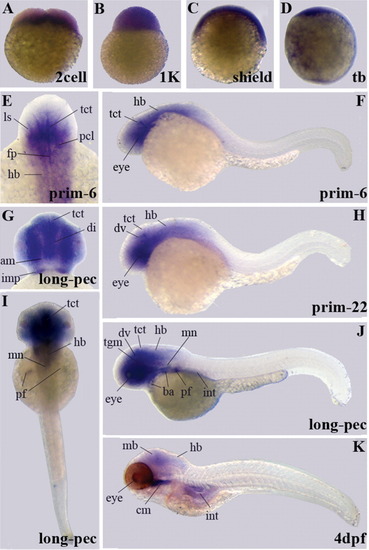
Gene expression patterns of enigma variants encoding the PDZ domain. Expression was detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization in eight different developmental stages. Embryos shown are at the 4-cell stage (indicating cleavage period), 1K-cell stage around mid-blastula transition (MBT), shield stage at mid-gastrulation, and tail bud (tb) stage at end of gastrulation. All early embryos are shown in the lateral view. Furthermore, embryos at prim-6, prim-22, and long-pec stages refer to the pharyngula period and embryos at 4 days postfertilization (dpf) represent the early larval period. Lateral view of these embryos is shown in Figure 2F,H,J,K. Additionally, close-ups of frontal (E) and lateral (G) views and a dorsal view (I) of embryos at the long-pec stage are presented. am, adductus mandibulae; ba, branchial arches; cm, cephalic musculature; ce, cerebellum; hb, hindbrain; imp, intermandibularis posterior; int, intestine; ls, lens; mb, midbrain; ov, otic vesicle; pf, pectoral fin buds; som, somites. |
|
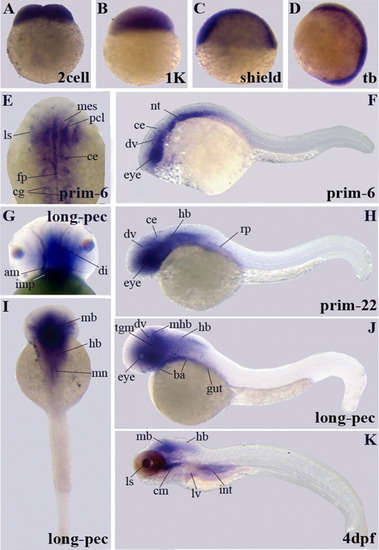
A-K: Gene expression patterns of enigma variants encoding the LIM domain by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Similar to the PDZ domain encoding variant, eight different developmental stages are shown. We present embryos at the two-cell stage during the cleavage period until at 4 days postfertilization (dpf) at the early larval period. F,H,J,K: Lateral views are shown for embryos at prim-6, prim-22, long-pec, and 4 dpf stages. F,G: A higher magnification of the dorsal view at prim-6 is shown in F and of the lateral view at the long-pec stage in G. The long-pec stage is also shown in I from a dorsal view. ba, branchial arches; ce, cerebellum; cm, cephalic musculature; dv, diencephalic vein; fp, floor plate; hb, hindbrain; int, intestine; ls, lens; mes, mesencephalon; mb, midbrain; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; ov, otic vesicle; pf, pectoral fin buds; pcl, proliferative cell layer; som, somites; tct, tectum; tgm, tegmentum. |
|
Gene expression patterns of enigma homologue variants encoding the PDZ domain. Expression results of whole-mount in situ hybridization are shown for the eight stages indicated. A-D,F,H-K: Additionally, for embryos between cleavage and end of gastrulation (A-D), we present lateral views of embryos at prim-6, prim-22, and long-pec stages in F,H,J,K and a dorsal view of an embryo at the long-pec stage in I. E: The dorsal view of the head of an embryo at stage prim-6 is shown at higher magnification. In G, we present a frontal view of the long-pec stage. am, adductus mandibulae; ba, branchial arches; cm, cephalic musculature; di, diencephalon; dv, diencephalic vein; fp, floor plate; hb, hindbrain; imp, intermandibularis posterior; int, intestine; mb, midbrain; ls, lens; mn, motor neurons; pf, pectoral fin buds; pcl, proliferative cell layer; tct, tectum; tgm, tegmentum. |
|
A-K: Gene expression patterns of enigma homologue variants encoding the LIM domain. Similar to the PDZ domain encoding variant, the results of whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis is shown for the eight stages indicated. F,H,J,K:Embryos at prim-6, prim-22, long-pec, and 4 dpf stages are shown in lateral view. I: A dorsal view of the long-pec stage is shown. E,G: Higher magnifications of expression domains in the head are presented for prim-6 in dorsal view (E) and for the long-pec stage in frontal view (G). am, adductus mandibulae; ba, branchial arches; cm, cephalic musculature; ce, cerebellum; cg, cranial ganglia; di, diencephalon; dv, diencephalic vein; fp, floor plate; hb, hindbrain; imp, intermandibularis posterior; int, intestine; mes, mesencephalon; mb, midbrain; mhb, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; ls, lens; lv, liver; mn, motor neurons; nt, notochord; pcl, proliferative cell layer; rf, roof plate; tct, tectum; tgm, tegmentum. |
|
Gene expression patterns of cypher variants encoding the LIM domain. Whole-mount in situ hybridization results for the eight developmental stages indicated are shown. F,H-K: Lateral views of embryos at prim-6, prim-22, long-pec, and 4 dpf stages (F,H,J,K), and I shows the dorsal view of the long-pec stage. E,G: A higher magnification of the lateral view of prim-22 in E and of the frontal view of the long-pec stage in G is presented. cm, cephalic musculature; h, heart; int, intestine; ls, lens; on, olfactory neurons; som, somites. |
|
Sections of whole-mount in situ hybridizations of long-pec stage embryos probed for both the PDZ and LIM domain encoding variants of enigma and enigma homologue. di, diencephalon; da, dorsal aorta; epp, exocrine pancreatic progenitor; gcl, ganglion cell layer; hb, hindbrain; ls, lens; mh, midbrain; nt, notochord; pi, pancreatic island; pf, pectoral fin buds; ret, retina; som, somites. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Effects of microinjections of enigma gene-specific morpholinos on zebrafish embryos. Embryos at the three-somite stage, six-somite stage, nine-somite stages and at prim6 are presented. A-D,I-l,Q,q,S,U,V: Control embryos are shown. E-H,M-p,R,r,T,W,X: The enigma morpholino-injected embryos. A-D: Lateral views of control embryos at the somite stages and 24 hpf are shown (Co). E-H: The enigma morpholino-injected embryos (Mo) are shown. I,J,Q: The myoD expression of control embryos at tail bud, six-somite, and prim6 stage in lateral view. Dorsal views of these embryos is presented in i,j,q. MyoD expression in morpholino-injected embryos is shown at tail bud, six-somite, and prim6 stage in both lateral (M,N,R) and dorsal (m,n,r) views. Lateral (K,L) and dorsal (k,l) views of no tail (ntl) expressing control embryos are shown for tail bud and six-somite stage. The same stages of morpholino-injected embryos expressing ntl are presented in lateral (O,P) and dorsal (o,p) views. In addition, control and morpholino-injected embryos at tail bud and six-somite stage probed for eve 1 and snail 1 expression are shown. Control embryos are depicted in lateral (S-V) and dorsal (s-v) views. Also, the corresponding morpholino-injected embryos are shown in lateral (W-Z) and dorsal (w-z) views. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
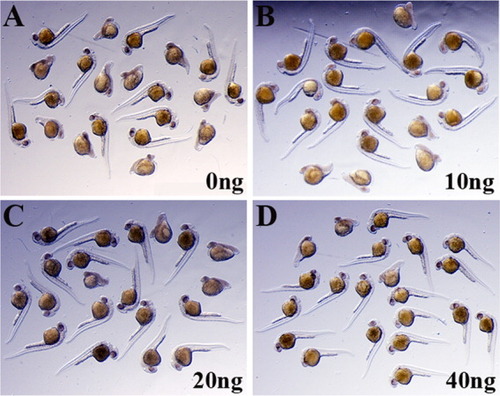
Rescue of enigma MO-induced phenotype. A rescue experiment as described in Table 2 (lower panel) was performed. Shown here are group pictures of embryos fixed at 24 hours postfertilization (hpf). All embryos shown in A-D were injected at the one-cell stage with 2 ng of enigma MO-2. Embryos in B-D were co-injected with indicated amounts of enigma full-length RNA (10, 20, and 40 pg, respectively). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. |
|
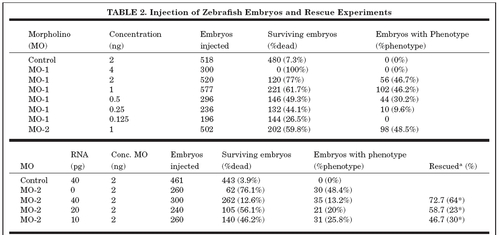
aThe asterisks indicate percentage of rescued embryos not including mortality as an aspect of rescue. PHENOTYPE:
|