- Title
-
Na,K-ATPase α2 and Ncx4a regulate zebrafish left-right patterning
- Authors
- Shu, X., Huang, J., Dong, Y., Choi, J., Langenbacher, A., and Chen, J.N.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Na,K-ATPase α2 is required for heart and gut LR patterning in zebrafish. (A-D) Live 2-day-old control (A), α2 morphant (B), Ncx4a morphant (C) and A23187-treated (D) embryos. (E-G) α2 morphants that exhibited normal (E), absent (F) or reversed (G) cardiac looping after 2 days of development. Ventral view, with anterior to the top. v, ventricle; a, atrium. (H-J) 2-day-old α2 morphants with normal (H), straight (I) or reversed (J) positions of gut, liver and pancreas. Dorsal view, with anterior to the top. li, liver; p, pancreas. (K) Bar chart detailing the heart and gut laterality phenotypes of uninjected embryos and those injected with CTL-MO, α2-MO, α2-SP-MO, Ncx4a-MO and Ncx4a-SP-MO. The effects of α2-SP-MO and Ncx4a-SP-MO on RNA processing are shown in the upper and lower panels, respectively, on the right. |
|
Na,K-ATPase α2 is required for asymmetric gene expression in zebrafish. Examples of spaw (A-D), pitx2c (E-H), lft1 (I-K) and lft2 (L-N) expression pattern in α2-MO-injected embryos at the 15-, 22- or 24-somite stage. Dorsal view, anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
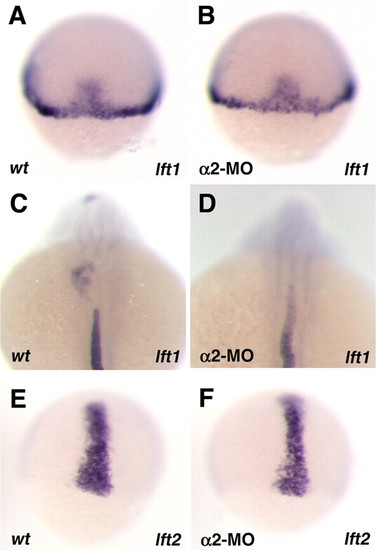
The expression of lft1 and lft2 in zebrafish α2 morphants. Examples of lft1 (A-D) and lft2 (E,F) expression in wild type (wt, A,C,E) and α2 morphants (B,D,F) at the shield stage (A,B), 75% epiboly (E,F) and 22-somite stage (C,D). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
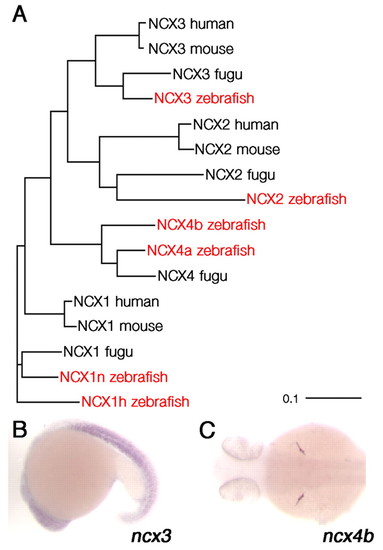
Phylogenetic analysis of zebrafish NCX isoforms and expression patterns of ncx3 and ncx4b. (A) The sequences of zebrafish ncx1h, ncx1n, ncx3 and ncx4a were derived from RACE and RT-PCR. Full-length zebrafish ncx2 and ncx4b sequences were obtained from the Ensembl Genome Browser. The amino acid sequences of human, mouse and fugu NCX isoforms are the same as those used by Marshall et al. (Marshall et al., 2005). Sequence alignments and phylogenetic analyses were performed using ClustalX. The unit of the scale bar represents 10% amino acid substitution per site. (B) ncx3 is expressed predominantly in the somites in 1-day-old zebrafish embryos. (C) ncx4b expression is restricted in the hypaxial muscle after 3 days of development. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Ncx4a is required for heart and gut LR patterning in zebrafish. (A-F) Expression pattern of the genes encoding Na,K-ATPase α2 and Ncx4a. Transcripts encoding Na,K-ATPase α2 (A) and Ncx4a (D) are detected prior to the mid-blastula stage. By the 10-somite stage, Na,K-ATPase α2 (B) and Ncx4a (E) are expressed in a broad range of tissues including Kupffer's vesicle (kv, arrow). By the 24-somite stage, Na,K-ATPase α2 is expressed predominantly in the somites (C), whereas Ncx4a remains ubiquitous (F). (G) Bar chart of the percentage of embryos exhibiting heart and/or gut laterality defects. |
|
Na,K-ATPase α2 and Ncx4a in DFCs/KV are required for LR patterning. (A) Morpholino knockdown of genes encoding Na,K-ATPase α2 or Ncx4a in DFCs induces LR patterning defects in zebrafish. Bar chart shows the percentage of embryos injected with α2-MO or Ncx4a-MO developing cardiac looping defects. (B,C) Fluorescent signals of the α2-MO accumulated in DFCs in embryos injected with the MO at the 128-cell stage (B), but were largely excluded from DFCs when the injection was done at the dome stage (C). Arrows point to DFCs. (D,E) The expression pattern of ntl in α2 morphants (E) is similar to that observed in CTL-MO-injected embryos (D). (F,G) The morphology of KV (arrowheads) appears normal in control (F) and α2-MO-injected (G) embryos. (H,I) Anti-acetylated tubulin staining shows that cilia are present in KV of control (H) and α2-MO-injected (I) embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
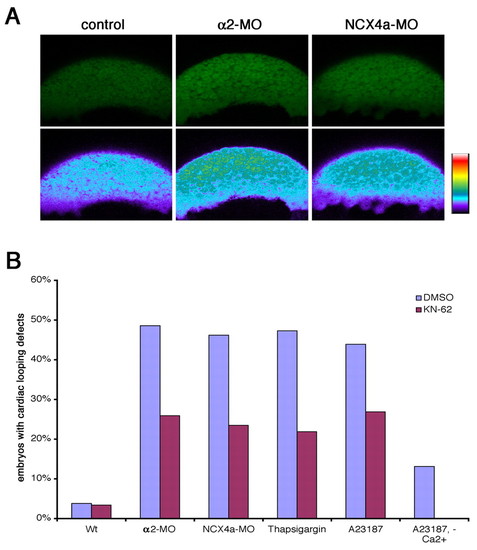
CaMKII inhibition suppresses LR defects induced by altered Ca2+ levels. (A) Confocal imaging of Calcium Green in blastomeres of control zebrafish embryos (left) and those injected with α2-MO (middle) and Ncx4a-MO (right). The upper panels show the original fluorescent images and the lower panels are false-colored to highlight the increased Ca2+ levels in α2 and Ncx4a morphants. (B) CaMKII mediates Ca2+ signaling in LR patterning. Bar chart shows the percentage of embryos exhibiting LR patterning defects. Treatment with the CaMKII-inhibitor KN62 is able to block LR patterning defects induced by α2-MO, Ncx4a-MO, A23187 or thapsigargin. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|