- Title
-
A transgenic Lef1/beta-catenin-dependent reporter is expressed in spatially restricted domains throughout zebrafish development
- Authors
- Dorsky, R.I., Sheldahl, L.C., and Moon, R.T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
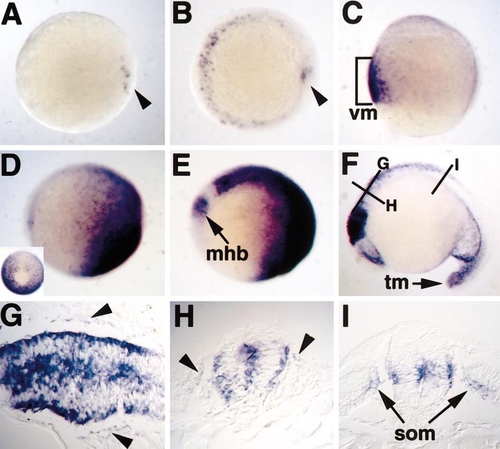
TOPdGFP expression reflects known domains of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Animal pole views are shown in (A) and (B). Lateral views are shown in (C–F), with ventral to the left in (C) and anterior to the left in (D–F). (A) At dome stage (4 hpf), expression is localized to deep marginal cells on one side of the embryo, (arrowhead). (B) By shield stage, expression is observed in the ventrolateral marginal region and in the shield hypoblast (arrowhead). (C) At 80% epiboly, GFP expression expands throughout the ventral mesoderm (vm). (D) Following gastrulation, mRNA is enriched at the posterior (right) end of the embryo. (Inset) Tailbud view shows exclusion of mRNA in the notochord (top). (E) At the six-somite stage, the first expression in the nervous system is seen at the presumptive midbrain/hindbrain boundary (mhb) and hindbrain, with an obvious gap between these regions. (F) By 18 somites, strong GFP expression is present in the midbrain region, with weaker expression in the ventral forebrain and tail mesoderm (tm). Lines indicate planes of section in (G–I). (G) Longitudinal section at 18 somites, showing expression throughout the hindbrain and medial neural crest cells (arrowheads). (H) Transverse section through the hindbrain, with medial neural crest cells marked by arrowheads. (I) Transverse section through the spinal cord, illustrating expression in the dorsomedial somite (som) closest to the neural tube, and in an intermediate zone of the CNS. |
|
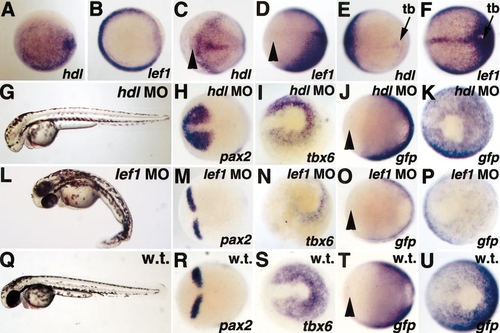
Reporter expression requires lef1, but not hdl, activity. Animal pole views are shown in (A) and (B). Anterior views with dorsal to the right are shown in (C, D, H, J, M, O, R, T). Posterior views with dorsal to the left are shown in (E, F, I, K, N, P, S, U). Arrowheads mark the rostral limit of the neurectoderm. At shield stage, hdl is expressed throughout the epiblast (A), while lef1 is expressed primarily in the germ ring (B), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to Fig. 1B). At bud stage, hdl is expressed in the anterior neurectoderm and underlying prechordal plate (C), while lef1 expression is absent in this region (D), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to T). hdl is expressed very weakly in the tailbud (tb) at bud stage (E), while lef1 is expressed at high levels in this region (F), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to U). Injection of a hdl morpholino phenocopies the hdl mutant at 36 hpf, causing loss of telencephalon and eyes (G). The hdl morpholino results in rostral expansion of pax2 (compare H and R), but has no effect on tbx6 expression (compare I and S). Loss of hdl has no effect on expression of TOPdGFP in the anterior neurectoderm (compare J and T) or in the tailbud (compare K and U). Injection of a lef1 morpholino results in loss of tail structures posterior to the yolk extension at 36 hpf (L). While the lef1 morpholino has no effect on pax2 expression (compare M and R), it significantly decreases tbx6 (compare N and S). Similarly, loss of lef1 has no effect on anterior TOPdGFP expression (compare O and T), but it significantly decreases expression in the tailbud (compare P and U). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
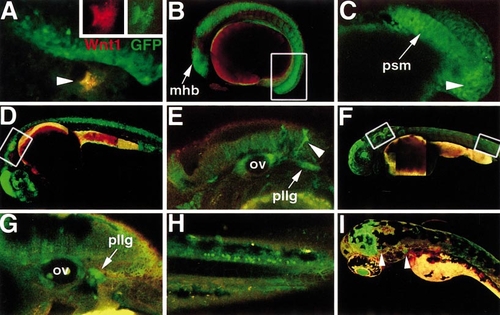
TOPdGFP reporter expression is Wnt-responsive and dynamic throughout development. (A) Following injection with DNA encoding Wnt1-myc, ectopic reporter expression is induced outside the endogenous domain of GFP (arrowhead). (Inset) This cell expresses both Wnt1-myc, as detected by anti-myc immunostaining (red), and GFP (green). In all following panels, red autofluorescence is shown for contrast. (B) Twelve-somite embryo. mhb, midbrain/hindbrain boundary. Box indicates region depicted at higher power in (C). (C) GFP is strongly expressed in the tail epiblast and hypoblast (arrowhead) and presomitic mesoderm (psm). (D) 24-hpf embryo. Box indicates region depicted at higher power in (E). (E) GFP is present at low levels in the brain and higher levels in the otic vesicle (ov), migrating pigment cells (arrowhead), and posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg). (F) 48-hpf embryo. Left box indicates region depicted in (G) and right box indicates region depicted in (H). (G) While expression decreases in the otic vesicle (ov), it is maintained at a high level in the posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg). (H) High-power view of the posterior spinal cord shows specific TOPdGFP expression in individual neurons. (I) 72-hpf embryo. GFP is expressed in the dorsal midbrain, lens, and cranial ganglia (arrowheads). |
|
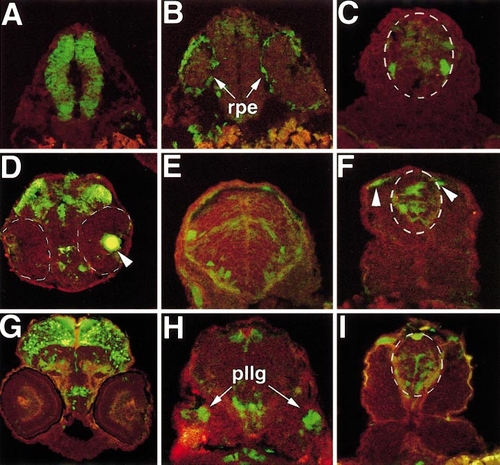
Transverse cryosections of transgenic embryos show localized expression in regions of the CNS and other tissues. In all panels, red autofluorescence is shown for contrast. Spinal cord is outlined in white dotted lines in (C, F, I). (A–C) 24 hpf; (D–F) 36 hpf; (G–I) 48 hpf. (A) Midbrain rostral to the eye is shown. (B) Section through caudal eye region. rpe, retinal pigmented epithelium. (C) Spinal cord section, showing individual GFP-labeled neurons. (D) Eye and midbrain region. Eyes are outlined in white dotted lines, lens is indicated by arrowhead. (E) Hindbrain section. Individual neurons in the ventral hindbrain express GFP. (F) In the spinal cord, expression is seen at multiple dorsal/ventral positions and in dorsal pigment cells (arrowheads). Pigment cells are identifiable by their morphology and position just below the ectoderm. (G) Extensive GFP expression is present in the dorsal midbrain. (H) Section just caudal to ear. pllg, posterior lateral line ganglion. (I) Spinal cord expression is similar to domains observed at 36 hpf. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 241(2), Dorsky, R.I., Sheldahl, L.C., and Moon, R.T., A transgenic Lef1/beta-catenin-dependent reporter is expressed in spatially restricted domains throughout zebrafish development, 229-237, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.