- Title
-
A truncating mutation in CEP55 is the likely cause of MARCH, a novel syndrome affecting neuronal mitosis
- Authors
- Frosk, P., Arts, H.H., Philippe, J., Gunn, C.S., Brown, E.L., Chodirker, B., Simard, L., Majewski, J., Fahiminiya, S., Russell, C., Liu, Y.P., Hegele, R., Katsanis, N., Goerz, C., Del Bigio, M.R., Davis, E.E.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Med. Genet.
|
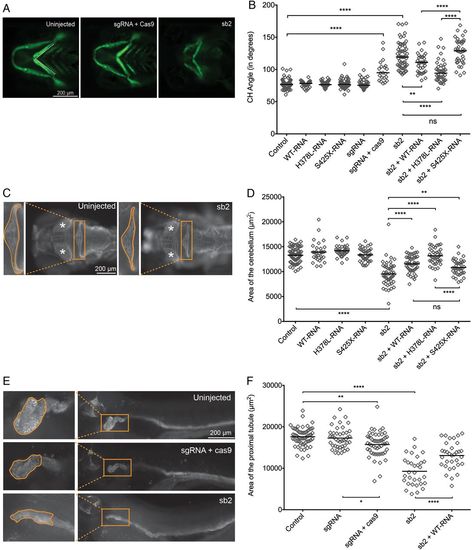
Transient suppression or CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome-editing of cep55l results in craniofacial, neurological and renal abnormalities in zebrafish. (A) Representative live ventral views of 4 dpf -1.4col1a1:eGFP larvae showing craniofacial structures. cep55l F0 mutants or sb2 morphant larvae show significantly broader ceratohyal (CH) angles compared with controls. (B) Plot indicates the measurement of the ceratohyal angle (as shown in panel A). RNA injected alone shows no effect. Larvae injected with sb2 or sgRNA+Cas9 display significantly increased ceratohyal angle compared with controls. This phenotype can be rescued with coinjection of sb2 and wild-type (WT) (p.H378-RNA) or p.L378-RNA. sb2+S425X RNA does not rescue significantly. n=23–62 embryos/injection; repeated. (C) 4 dpf larvae stained for acetylated tubulin show hypoplasia of brain regions, including the cerebellum and optic tecta. Box and zoomed image indicate the cerebellum; asterisks (*) indicate optic tecta. (D) Plot indicates the quantification of the total area (µm2) of the cerebellum at 4 dpf, as indicated by orange outline in the control and sb2 insets of (C). n=31–81 embryos/injection; repeated. (E) Larvae fixed at 4 dpf and stained for Na+/K+ATPase are shown (lateral view; zoomed image represents the proximal convoluted tubule; outline indicates the area quantified in (F). Embryos injected with cep55 sb2 or sgRNA + Cas9 display proximal tubules of decreased area (µm2) and decreased presence of convolutions compared with control embryos. (F) Plot indicates the total area (µm2) of the proximal tubule in 4 dpf larvae; n=31–61 embryos/injection, repeated. *, **, *** and **** indicate p<0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001 respectively. ns, not significant. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
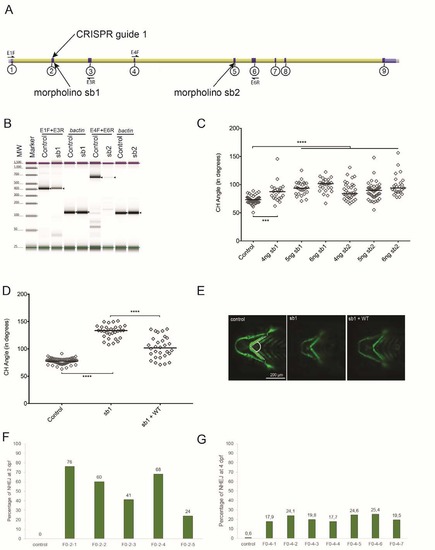
Efficiency of morpholinos (MOs) and CRISPR sgRNA targeting cep55l. (A) Schematic of the Danio rerio cep55l locus showing the location of the two MOs and the CRISPR guide target sites. Exons are indicated with circled numbers. (B) TapeStation electrophoresis of RT-PCR products showing sb1 and sb2 morpholino efficiency. Sequencing of cloned PCR fragments showed that sb1 produces a 45 bp retention of intronic sequence, and sb2 results in deletion of 242 bp; both result in premature termination codons. Expected bands are indicated with black arrows; primer locations are indicated in panel A; [sic]-actin was amplified to control for cDNA integrity. (C) Dose curve of sb1 and sb2 MOs. Embryo batches were injected with increasing amounts of MO, imaged live at 4 dpf, and the angle of the ceratohyal (CH) cartilage was measured (See panel E); n=22-59 embryos/injection. (D) Plot representing the effects of sb1 and sb1 + WT-RNA injections on 4 dpf -1.4col1a1:egfp larvae. sb1 induces a significant increase in the CH angle compared to uninjected controls. Co-injection of WT-RNA with sb1 rescues significantly the CH angle. n= 20-63 embryos/injection, repeated. (E) Representative live ventral images of 4 dpf -1.4col1a1:egfp larvae demarcate cartilage structures with the presence of GFP-positive cells. CH angle was measured as shown (dashed white lines). (F) Estimation of mosaicism in cep55l F0 mutant embryos harvested at 2 dpf as assessed by cloning of PCR products flanking the targeting site and Sanger sequencing. (G) Assessment of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing efficiency using next generation sequencing of PCR products amplified from genomic DNA of control and cep55l F0s (n=7) harvested at 4 days post fertilization. NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; **** indicates p<0.0001. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
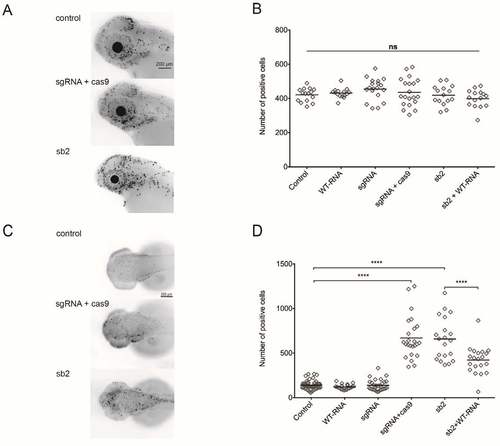
Apoptosis and cell cycle markers (M-phase) quantified in cep55l morphants and F0 mutants. (A) Larvae were fixed at 2 days post fertilization and stained with rabbit IgG polyclonal p-Histone H3 (Ser 10)-R antibody to highlight the presence of dividing cells in the anterior structures of the zebrafish central nervous system. Representative lateral views of inverted fluorescent images are shown. (B) Plot represents the quantification of fluorescent signals marked by the pH3 (Ser 10)-R antibody for each injected condition. All injected conditions listed display no significant differences from one another. n=15-20 embryos/injection. (C) Larvae were fixed at 2 dpf and stained with the ApopTag rhodamine in situ Apoptosis Detection kit (Chemicon) to detect apoptotic cells. Representative dorsal views are shown (D) Plot representing the number of ApopTag rhodamine positive cells per injected condition. sgRNA + Cas9 injected embryos display an increase of apoptotic markers compared to both uninjected and sgRNA-alone conditions. n=20-58 embryos/condition, repeated. **** indicates p<0.0001; ns, not significant. PHENOTYPE:
|