- Title
-
Kit-like immunoreactivity in the zebrafish gastrointestinal tract reveals putative ICC
- Authors
- Rich, A., Leddon, S.A., Hess, S.L., Gibbons, S.J., Miller, S., Xu, X., and Farrugia, G.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
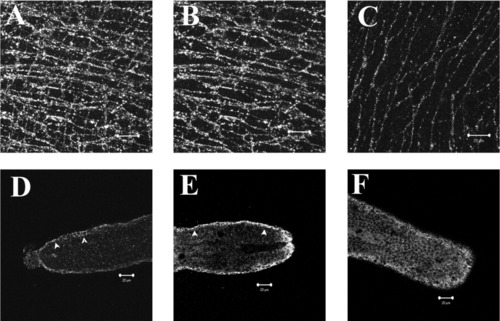
Anti-Kit rabbit polyclonal antibody identifies putative ICC networks in the adult zebrafish GI tract. Full thickness confocal stack reconstruction of an adult zebrafish GI whole mount preparation immunostained using rabbit anti-Kit polyclonal antibody (A). Total thickness of reconstructed stack ≈20 μm. Reconstruction of a partial thickness stack (≈8-μm-thick) shows a kit-positive network in the myenteric plexus region with stellate-shaped, highly branching cells (B). A second distinct network of slender bipolar cells oriented parallel to the circular smooth muscle cells was located closer to the submucosal border and is shown in a partial stack reconstruction of a 6-μm-thick region (C). Kit-like immunoreactivity was observed in the GI tract of zebrafish larvae beginning at 7 dpf. Single confocal sections approximately 0.6-μm-thick of mid-saggital sections from the posterior end of the larvae GI tract show branching cells with slender processes in the tunica muscularis (D, arrows). Background staining of the mucosal layer prevented full-thickness stack reconstruction. The density of Kit-positive cells was increased at 11 dpf (E), and a network of Kit-positive cells was observed at 20 dpf (F). Scale bars = 20 μm. |
|
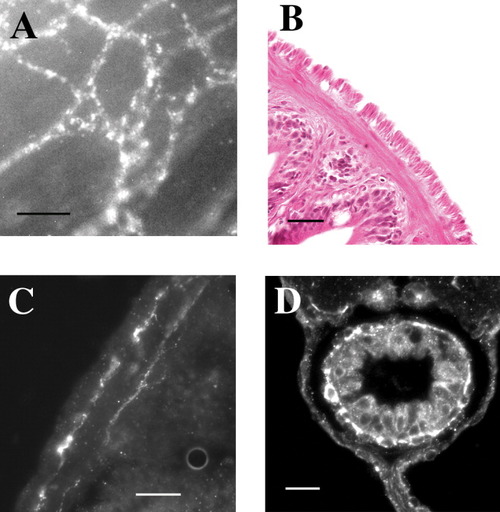
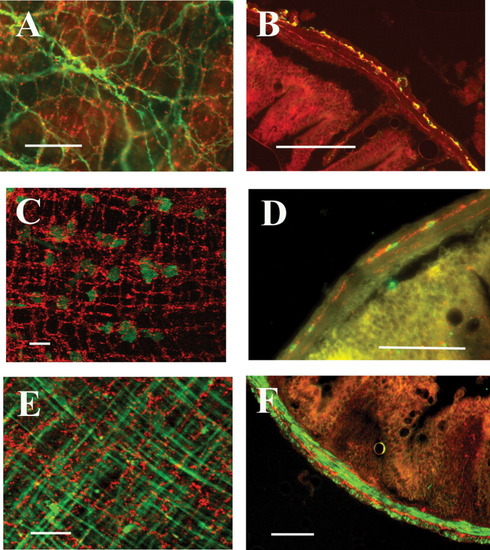
Cells with Kit-like immunoreactivity form a dense network in the myenteric plexus region, and a second network close to the circular smooth muscle-submucosal border. High magnification of Kit-positive cells reveals individual stellate-shaped cells (white) in a full thickness stack (A). Circular and longitudinal muscle layers of the adult GI tract are clearly observed in H&E stained transverse sections (B). Kit-positive cells are found in the myenteric plexus region, and a thin layer of Kit-positive cells is located near the circular smooth muscle-submucosal border (C). A single layer of Kit-positive cells was observed in the tunica muscularis of transverse sections of zebrafish larvae (white arrow) (D). Scale bars = 20 μm. |
|
Cells with Kit-like immunoreactivity form a dense network in the myenteric plexus region, and a second network close to the circular smooth muscle-submucosal border. High magnification of Kit-positive cells reveals individual stellate-shaped cells (white) in a full thickness stack (A). Circular and longitudinal muscle layers of the adult GI tract are clearly observed in H&E stained transverse sections (B). Kit-positive cells are found in the myenteric plexus region, and a thin layer of Kit-positive cells is located near the circular smooth muscle-submucosal border (C). A single layer of Kit-positive cells was observed in the tunica muscularis of transverse sections of zebrafish larvae (white arrow) (D). Scale bars = 20 μm. |
|
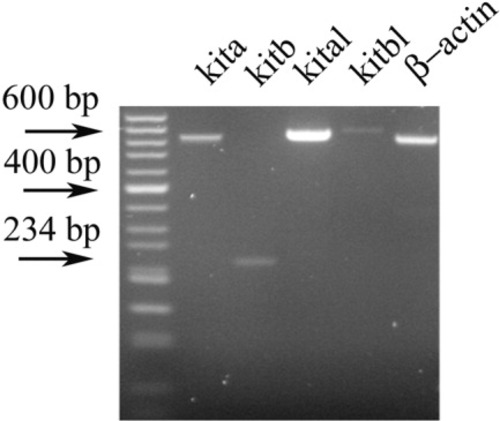
RT-PCR amplifies the zebrafish Kit receptor tyrosine kinase kita and kitb, and Steel factor, kitla and kitlb, from isolated adult GI tract. Amplification products are shown for primer sets designed for each gene (Table 1), and for β-actin. Products of correct size for each primer set were observed and confirmed by sequencing. |
|
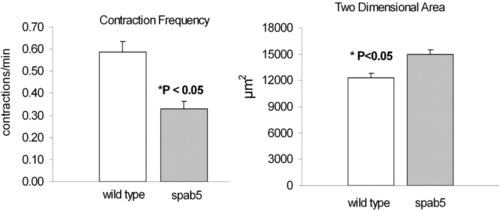
The pigment pattern mutation Sparse, a kita null mutant, has decreased spontaneous GI contractions and an increased size of the GI tract. Optically transparent zebrafish larvae (7 dpf) were videotaped and contraction frequency was 0.59 ± 0.05 contractions/minute (mean ± SE, n = 20) in wild type, and 0.33 ± 0.03 contractions/minute (P < 0.05, n = 23) in homozygous Sparse mutant larvae. Cross-sectional area of the GI tract was measured in single frames for each experiment. Cross-sectional area was less for wild-type, 12,331 ± 467, compared to the Sparse mutant larvae, 14,985 ± 483 (P < 0.05). |

Unillustrated author statements |