PUBLICATION
ubtor Mutation Causes Motor Hyperactivity by Activating mTOR Signaling in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Wang, T., Zhou, M., Zhang, Q., Zhang, C., Peng, G.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-210728-35
- Date
- 2021
- Source
- Neuroscience Bulletin 37(12): 1658-1670 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Peng, Gang, Zhang, Cuizhen
- Keywords
- Epilepsy, Hyperactivity, Ubtor, Zebrafish, mTOR
- MeSH Terms
-
- Animals
- Mutation/genetics
- Zebrafish*/metabolism
- TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases/genetics
- TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases/metabolism
- PubMed
- 34309811 Full text @ Neurosci. Bull.
Abstract
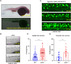
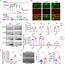
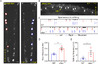
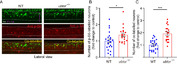
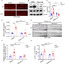
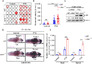
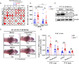
Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling governs important physiological and pathological processes key to cellular life. Loss of mTOR negative regulators and subsequent over-activation of mTOR signaling are major causes underlying epileptic encephalopathy. Our previous studies showed that UBTOR/KIAA1024/MINAR1 acts as a negative regulator of mTOR signaling, but whether UBTOR plays a role in neurological diseases remains largely unknown. We therefore examined a zebrafish model and found that ubtor disruption caused increased spontaneous embryonic movement and neuronal activity in spinal interneurons, as well as the expected hyperactivation of mTOR signaling in early zebrafish embryos. In addition, mutant ubtor larvae showed increased sensitivity to the convulsant pentylenetetrazol, and both the motor activity and the neuronal activity were up-regulated. These phenotypic abnormalities in zebrafish embryos and larvae were rescued by treatment with the mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin. Taken together, our findings show that ubtor regulates motor hyperactivity and epilepsy-like behaviors by elevating neuronal activity and activating mTOR signaling.
Genes / Markers
Expression
Phenotype
Mutations / Transgenics
Human Disease / Model
Sequence Targeting Reagents
Fish
Orthology
Engineered Foreign Genes
Mapping