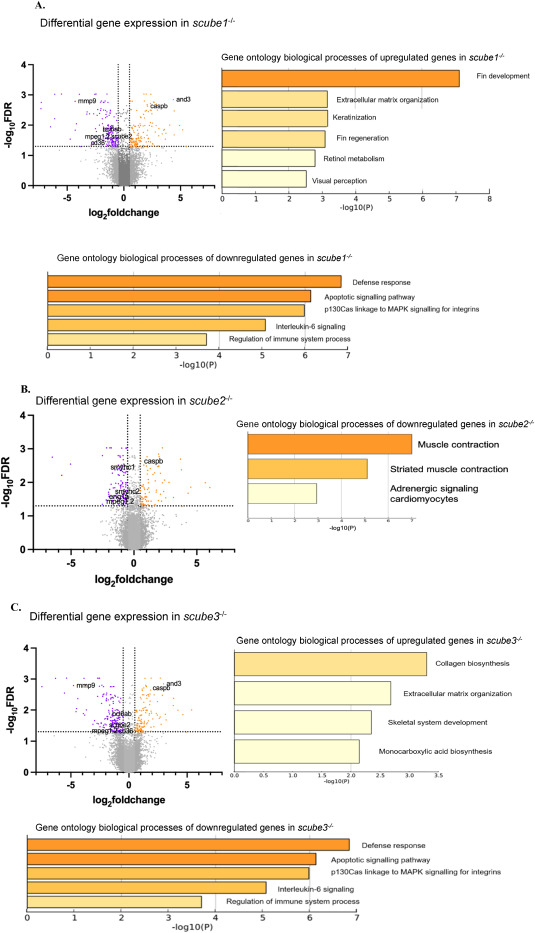
Fig. 4 RNA seq analysis of scube1−/−, scube2−/−and scube3−/−embryos at 30 hpf. (A) RNA sequencing of scube1 mutants revealed upregulation of processes related to fin development and regeneration, extracellular matrix formation, keratinisation, and eye development. Conversely, there is a downregulation of processes associated with the immune response system (response to bacterium, interleukin-6 signalling, response to wounding, platelet degranulation Herpes infection), apoptotic signalling and response to estrogen. (B) RNA sequencing of scube2−/− zebrafish mutants indicated downregulation of processes linked to muscle contraction and adrenergic signalling in cardiomyocytes. (C) RNA sequencing of scube3−/− zebrafish mutants revealed upregulation of processes related to collagen synthesis, extracellular matrix formation, and skeletal system development. Conversely, downregulated processes include those involved in the defence response system, specifically interleukin-6 signalling and the regulation of immune system processes. Yellow bars indicate lower significance or enrichment, while orange bars indicate higher values. FDR cutoff = 0.05. Volcano plots displaying differential gene expression between scube mutants and wild-type zebrafish. The x-axis shows log2 fold change in gene expression, and the y-axis indicates - log10 FDR. Each point represents an individual gene. Genes with absolute log2 fold change greater than 0.5 and FDR less than 0.05 are highlighted: upregulated genes are orange, downregulated genes are purple, and non-significant genes are grey.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, , Tran, Q.D., Mirkovic, I., Miles, L.B., Berger, J., Wood, A.J., Ruparelia, A.A., Shehni, S.A., Currie, P.D., Redundant and novel functions of scube genes during zebrafish development, , Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.