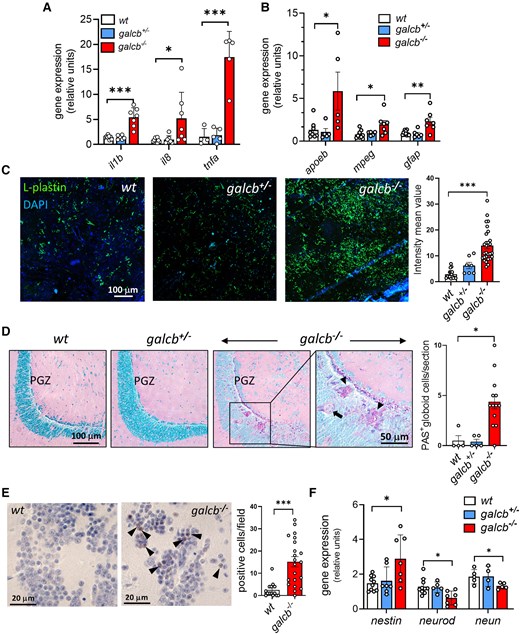
Fig. 4 Brain neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in galcb knockout zebrafish. (A and B) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression of neuroinflammation-related genes interleukin-1b (il1b), il8, tumor necrosis factor-a (tnfa), apolipoprotein Eb (apoeb), macrophage expressed 1 (mpeg1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (gfap) in the brain of wild-type (WT), galcb+/− and galcb−/− zebrafish at 4 months post fertilization (mpf). For each gene, the data were normalized to its expression in one WT animal. Data are the mean ± standard deviation of 5–7 animals per group. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis shows the presence of numerous L-plastin-positive cells in the brain of galcb−/− zebrafish at 4 mpf, absent in WT and galcb+/−siblings. 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used for nuclear counterstaining. Right: Quantification of L-plastin signal intensity in ≥7 microscopic fields/group. (D) Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining shows the presence of globoid cells (arrows) in the periventricular grey zone (PGZ) of the brain of galcb−/− zebrafish at 4 mpf, absent in WT and galcb+/−siblings. The number of PAS-positive globoid cells were counted in ≥4 microscopic sections/group. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis shows the increase of cleaved caspase3-positive cells in the brain of galcb−/− zebrafish at 4 mpf compared with WT siblings. The number of cleaved caspase3-positive cells were counted in at least 14 microscopic fields/group. (F) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression of neuronal marker genes nestin, neuronal differentiation 1 (neurod1) and RNA binding fox-1 homolog 3a (neun) in the brain of WT, galcb+/− and galcb−/− zebrafish at 4 mpf. For each gene, the data were normalized to its expression in one WT animal (n > 4 animals/group). Data are the mean ± standard deviation. One-way ANOVA (Tukey's multiple comparison test): *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. RT-qPCR = reverse transcriptase-quantitative PCR.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Brain