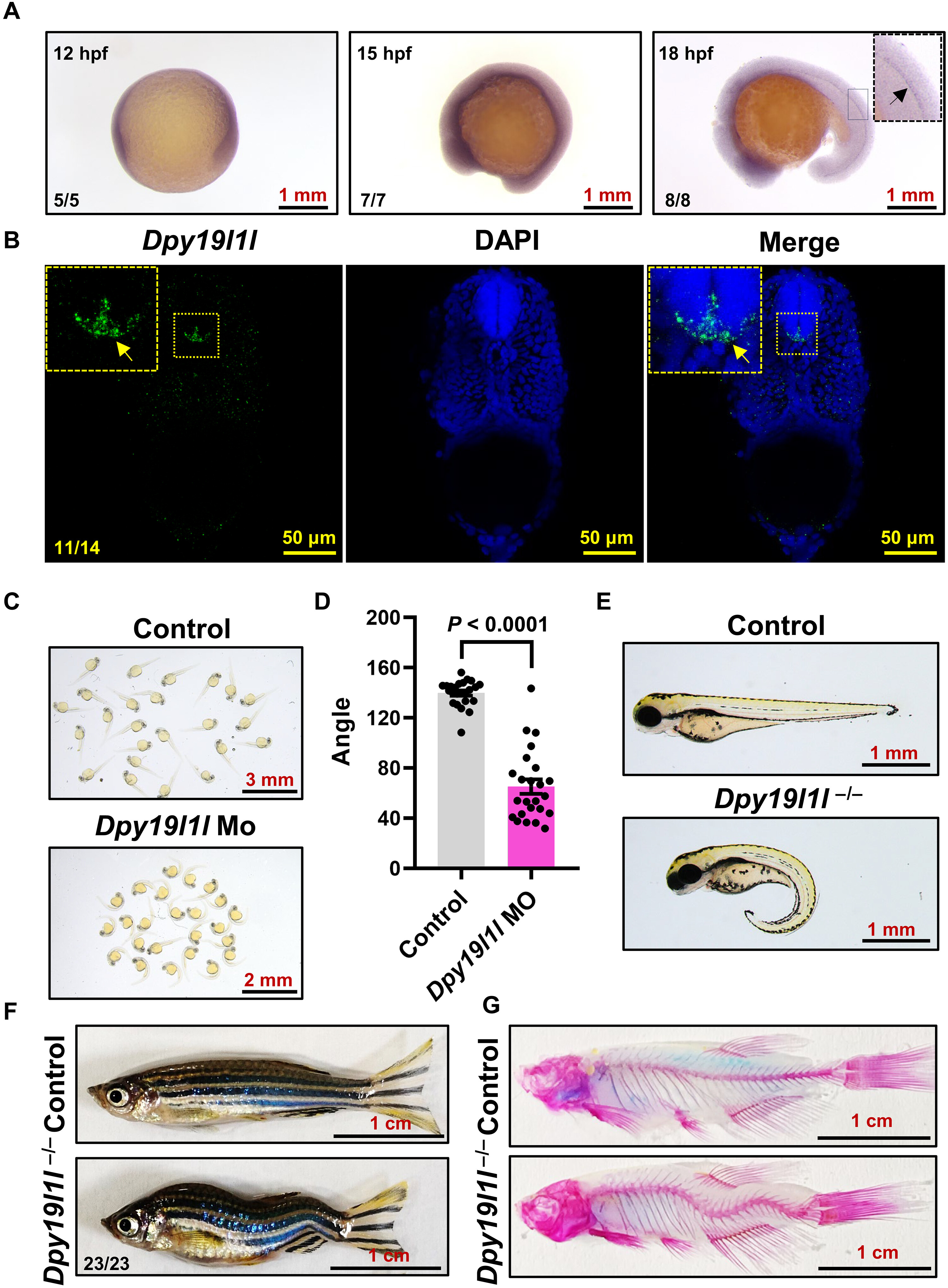
Fig. 1 Dpy19l1l expression in the spinal cord and its mutation leading to IS-like body axis curvature. (A) WMISH of dpy19l1l at 12 to 18 hpf. The arrow in the enlarged view of 18 hpf larvae indicates dpy19l1l expression. (B) Confocal projection of longitudinal trunk sections from 36 hpf larvae hybridized with a fluorescence riboprobe and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The yellow arrow in the enlarged view marks dpy19l1l expression in spinal cord floor plate cells. (C) Phenotypes of dpy19l1l MO-injected larvae at 36 hpf, showing body axis curvature. (D) Quantification of body axis angles using ImageJ (bar graph; means ± SEM, n = 24). The P value (unpaired t test) is indicated above bars. (E) External phenotypes of control sibling and dpy19l1l−/− mutants at 2 dpf. (F) External phenotypes of adult control sibling and dpy19l1l−/− mutants. (G) ARS staining of adult control sibling and dpy19l1l−/− mutants.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Sci Adv