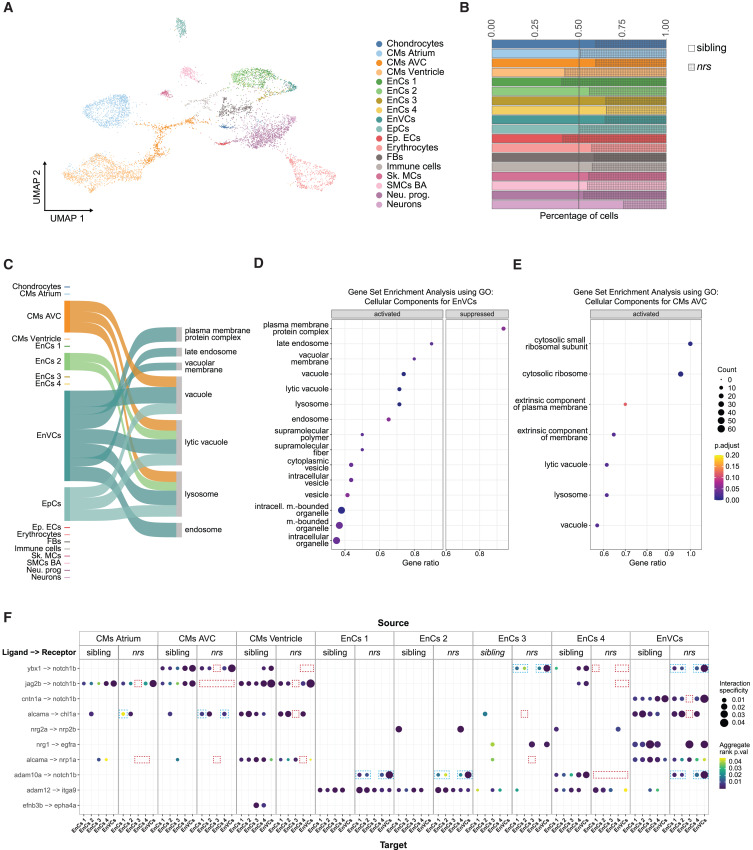
Fig. 6 Expression of lysosome related genes and notch1b-signalling is affected in nrs-mutants Results obtained from a snRNA transcriptome analysis of sibling and nrs mutant hearts at 3 dpf. (A) UMAP showing the various identified cell types from the snRNA-seq performed for mutant and sibling hearts at 3 dpf. (B) The proportion of different cell types observed in sibling versus mutant suggest that lysosomal impairment above all affects the representation of atrioventricular cardiomyocytes (CMs AVC), three endocardial populations (EnCs 3, EnCs 4) among them endocardial valve cells (EnVCs) and neurons in the larval heart. (C) Sankey diagram illustrates the cell-specificity of overrepresented lysosomal and membrane related gene pathways found in nrs mutants compared to siblings highlighting the relevance of lysosomal degradation in EnVCs. The width of the arrows is proportional to the number of differentially expressed genes in each cell cluster contributing to the pathway. (D and E) Gene set Enrichment Analysis using the differentially expressed genes between siblings versus mutants in EnVCs (D) and atrioventricular CMs (E), where ‘activated’ and ‘suppressed’ represent the pathways that are activated or suppressed in the mutant condition. The results obtained suggest an upregulated transcriptional response in mutant EnVCs and atrioventricular CMs to compensate impaired lysosomal function. (F) Ligand-receptor analysis from LIANA depicting the ligands from the source cells (top) to target cells (bottom) with ligand and receiving receptor shown on the y axis in the sibling and the mutant conditions. The ligand-receptor interactions affecting notch1b- and alcama-signaling are highlighted for the nrs mutant (red square = missing interaction, blue square = differing interaction).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ iScience