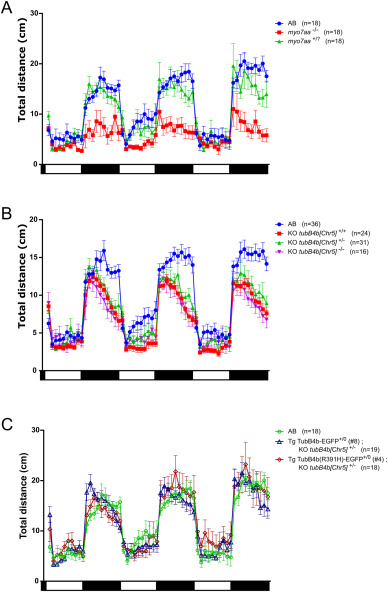
Fig. 9 Effect of dark and light exposure on 5 dpf zebrafish locomotion. A: total swimming distance traveled by wild-type larva (AB), myo7aa marty220d/ty220d homozygous larva (myo7aa−/−) or siblings myo7aa marty220d/+ & myo7aa mar+/+ larva (myo7aa+/?); n = 3 experiments. B: total swimming distance traveled by wild-type larva (KO tubB4b[Chr5]+/+), heterozygous knock-out larva (KO tubB4b[Chr5]+/−) and homozygous knock-out larva (KO tubB4b[Chr5]−/−); n = 6 experiments. C: total swimming distance traveled by wild-type larva (AB), Tg(tubB4b[Chr5]:TubB4b[Chr5]-EGFP)+/0; KO tubB4b[Chr5]+/− larva and Tg(tubB4b[Chr5]:TubB4b(R391H)[Chr5]-EGFP)+/0; KO tubB4b[Chr5]+/− larva. n = 3 experiments. Traveled distance was measured every minute. 10 min light (white rectangle) and dark (black rectangle) periods are represented below graph. Number of larvae is indicated next to genotype.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 517, Smaili, W., Pezet, C., Marlin, S., Ernest, S., R391 human dominant mutation does not affect TubB4b localization and sensory hair cells structure in zebrafish inner ear and lateral line, 301-316, Copyright (2024) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.