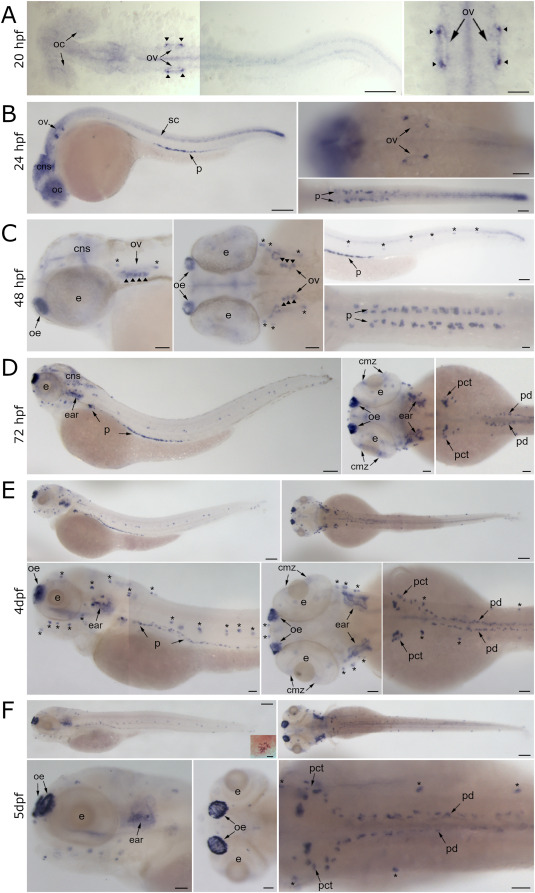
Fig. 2 Expression pattern of tubB4b[Chr5] mRNA during zebrafish embryo development. Whole mount in situ hybridization with tubB4b[Chr5]-specific antisense RNA probe in zebrafish larva. A: 20 hpf embryo; dorsal views. B: 24 hpf embryo; lateral view (left panel) and dorsal view focused on otic vesicle (top right) and tail (bottom right). C: 48 hpf embryo; lateral view (left panel) and dorsal view (central panel) of head; lateral view (top right panel) and dorsal view (bottom right panel) of tail. D: 72 hpf larva; lateral view (left panel) and dorsal view of head (central panel) and trunk (right panel). E: 4 dpf larva; lateral views (top and bottom left panels) and dorsal views (top right, central bottom and bottom right panels). F: 5 dpf larva; lateral views (top and bottom left panels) and dorsal views (top right, central bottom and bottom right panels). Insert within upper right panel shows one neuromast at high magnification. Flat mount (A) or whole mount (B–F) images. oc: optic cup; ov: otic vesicle; arrowhead: macular sensory hair cells; cns: central nervous system; sc: spinal cord; p: pronephros; e: eye; oe: olfactory epithelium; cmz: ciliary marginal zone; pct: proximal convoluted tubule; pd: pronephric duct; ∗: neuromast. Scale bar = 150 μm for whole embryo pictures, 50 μm for head or trunk excerpt and 10 μm for neuromast inset.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 517, Smaili, W., Pezet, C., Marlin, S., Ernest, S., R391 human dominant mutation does not affect TubB4b localization and sensory hair cells structure in zebrafish inner ear and lateral line, 301-316, Copyright (2024) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.