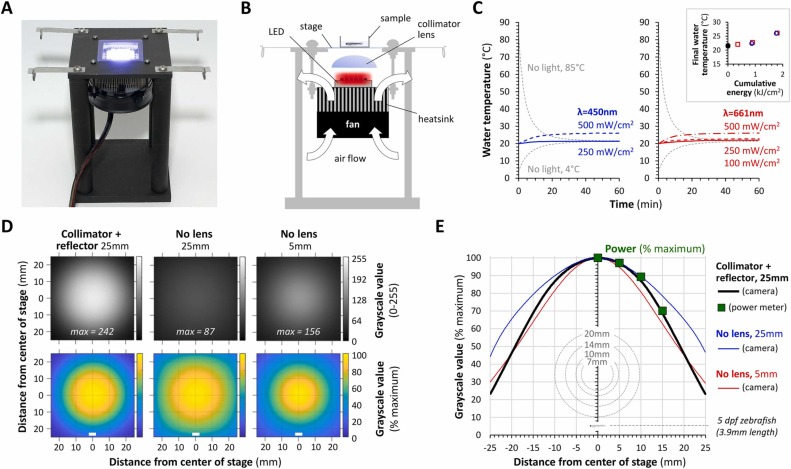
Fig. 1 LED light stand provides full-field illumination to larval zebrafish without heating the water. A: Photograph of the light stand. B: Schematic lateral projection of the light stand illustrating the locations of key components and the direction of airflow across the heatsink and heat exchanger. C: Bath temperature in a 35 mm MatTek dish placed in the center of the stage. The graphs show recordings during 1 h of exposure to a 450 nm blue LED (left) or 661 nm far red LED (right) at the powers indicated (expressed as mW/cm2 at the stage). Curves for water with initial temperatures of 85 °C or 4 °C (gray) equilibrating to room temperature are shown as controls to confirm that the thermistor functioned as expected. The inset panel shows the relationship between the final bath temperature after 1 h of light exposure, and the total light energy passing through the stage during the experiment (expressed as kJ/cm2); blue-outline squares show data from the 450 nm light source and red-outline circles from the 661 nm source. D: The spatial Illumination profile across the stage was measured by photographing a white plastic screen from above, while a 661 nm LED was illuminated with the stand in three different configurations: #1. LED 25 mm from stage with collimator lens and reflector (left column of images), #2. LED without lens or reflector, 25 mm from stage (center column); #3. LED without lens or reflector 5 mm from stage (right column). Top row: 8-bit grayscale images averaged from 20 pictures, using the same acquisition settings for each configuration. Bottom row: relative intensity color maps, in which each pixel was scaled to the brightest 0.5% of pixels in the averaged image for each configuration to compare spatial fall-off. The distance from the center of the stage is shown in mm. The white bars show the approximate size of a larval zebrafish at 5 dpf. E: Graph of relative light intensity as a function of distance from the center of the stage, calculated from the intensity colormap data in panel D. Colored lines are shown for each different configuration (configuration #1, black; configuration #2, blue; configuration #3, red). Verification of the photographic data from configuration #1 using a second method – positioning the center of a power meter sensor at different distances from the center of the stage – is shown as large green squares. For comparison, the coverslips of the standard sizes of glass-bottomed dishes used for zebrafish imaging, and a picture of a larval zebrafish at 5dpf, are superimposed below.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ J. Neurosci. Methods