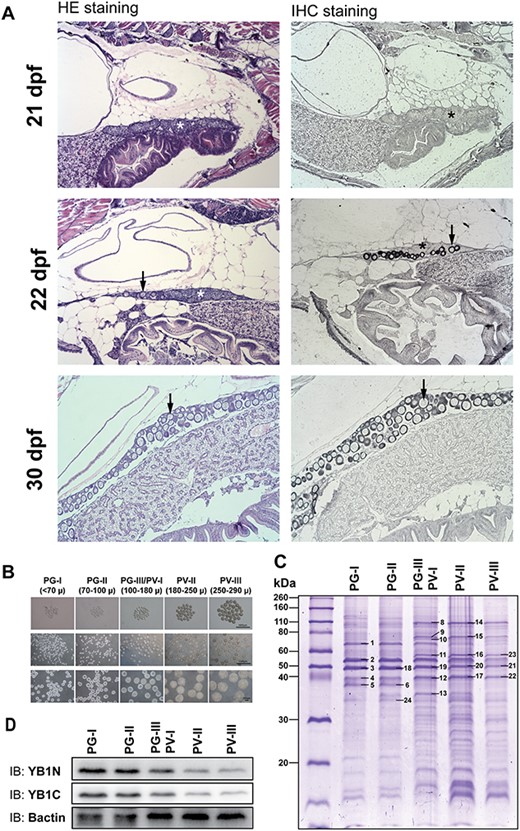
Fig. 4 Expression of Ybx1 during ovarian differentiation and follicle activation (PG–PV transition). (A) Immunohistochemical staining for Ybx1 protein during ovarian differentiation. The juvenile fish were sampled at 21, 22, and 30 dpf for histological sectioning and immunohistochemical staining. At 21 dpf, the germ cells or CN oocytes (asterisk) were clustered in cysts without follicle formation. Individual PN follicles (arrow) started to appear at 22 dpf and increased in number at 30 dpf. No signal for Ybx1 could be detected in the cystic CN cells; however, strong signals of Ybx1 appeared in the oocytes once follicles formed during cyst breakdown. (B) Sub-staging of PG and PV follicles. Based on size and morphological features, the PG stage is divided into early PG (PG-I), mid-PG (PG-II), and late PG (PG-III); and PV stage is divided into early PV (PV-I), mid-PV (PV-II), and late PV (PV-III). PG-III and PV-I were difficult to separate and therefore grouped together for analysis. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis for protein profiles during PG–PV transition. The PV-III/PV-I group represented the transitional stage. (D) Western blot for Ybx1 during PG-PV transition. (1) insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3; (2) Zgc:55673 protein; (3, 18–21) Y-box binding protein 1; (4, 12, 17, 22) actin; (8, 14) heat shock protein 90 kDa beta, member 1; (9, 15) heat shock protein 5; (10) heat shock protein 8; (11, 16, 23) procollagen-proline, 2-oxoglutarate 4-dioxygenase (proline 4-hydroxylase), beta polypeptide; (13) ribosomal protein lateral stalk subunit P0; (24) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Biol. Reprod.