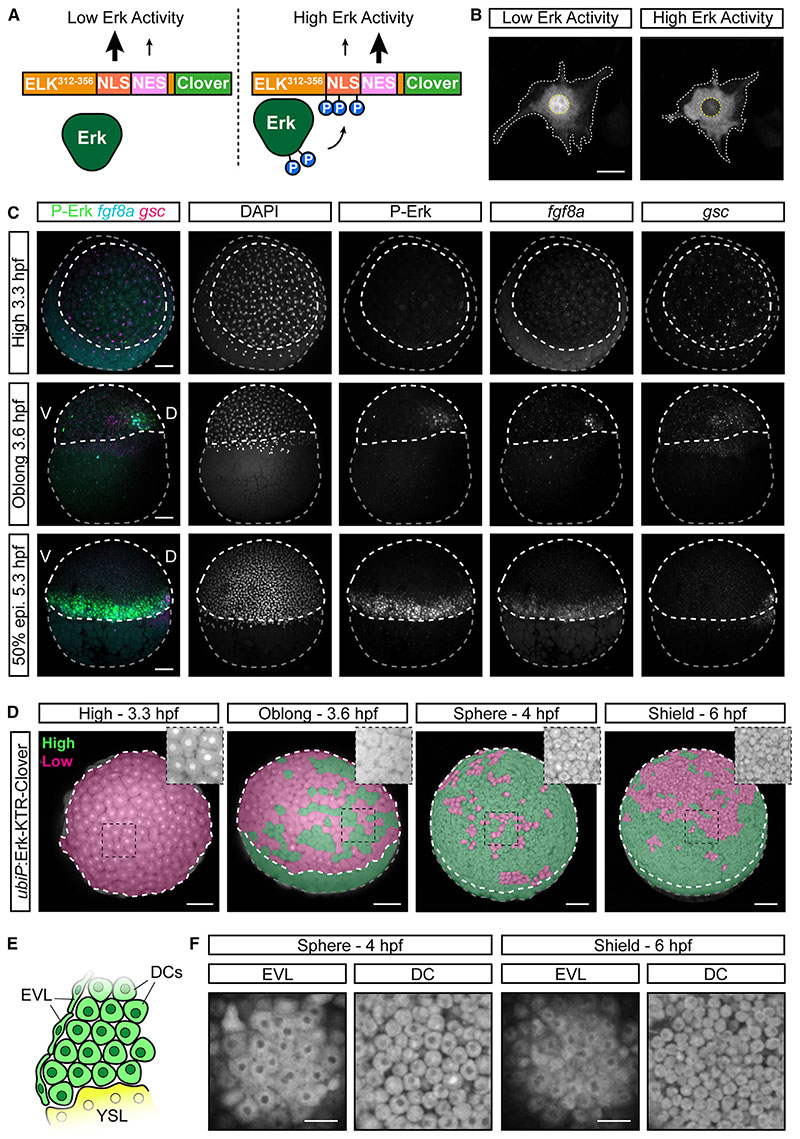
Figure 1 Off-target Erk-KTR activity in the early zebrafish embryo
(A) Schematic of the Erk-KTR construct showing the N-terminal Erk-docking domain derived from ELK1, a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) containing Erk-consensus phosphorylation sites (P), a nuclear export sequence (NES) and a C-terminal fluorescent protein, Clover.
(B) Live images of an NIH-3T3 cell transfected with
(C) Combined immunofluorescence and RNAscope showing diphosphorylated Erk (P-Erk) and
(D) Stills of live
(E) Schematic cross-section of the embryonic margin showing the relative position of the deep cells (DCs), the enveloping layer (EVL) and the yolk syncytial layer (YSL).
(F) Single
Scale bars, 25 μm (B), 50 μm (F), or 100 μm (C and D).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 58(23), Wilcockson, S.G., Guglielmi, L., Araguas Rodriguez, P., Amoyel, M., Hill, C.S., An improved Erk biosensor detects oscillatory Erk dynamics driven by mitotic erasure during early development, 2802-2818.e5, Copyright (2023) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell