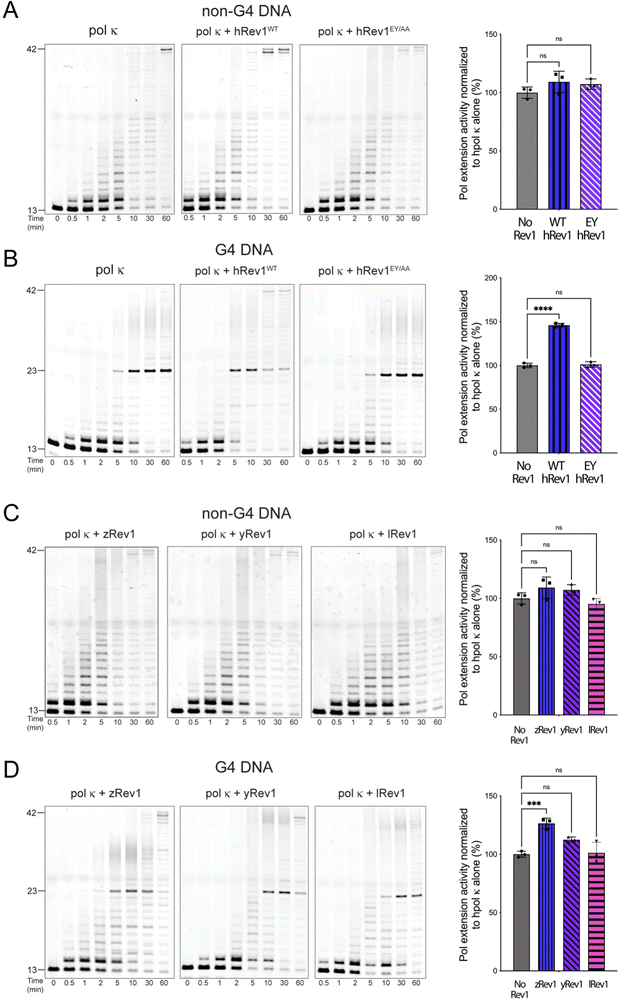
Fig. 5 Insert-2 is important for stimulation of processive DNA synthesis across a G4 motif by pol κ. Polymerase extension assays were performed to measure the impact of Rev1 on DNA synthesis by a more processive TLS pol. Briefly, human pol κ (10 nM) was incubated with 13/42-mer primer-template DNA (200 nM) for 15 minutes before the reaction was initiated by the addition of solution that contained Rev1 (50 nM), MgCl2 (5 mM), and dNTP solution (0.2 mM total; 50 μM each for dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP). Pol extension was allowed to proceed at 37 °C before quenching at the indicated timepoints. Substrate and products were separated by PAGE using 14% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels with 7 M urea. (A) Pol extension assay results are shown for 13/42-mer non-G4 DNA where pol κ was incubated alone or in the presence of either WT hRev1 or the EY mutant. (B) Pol extension assay results are shown for 13/42-mer G4 DNA where pol κ was incubated alone or in the presence of either WT hRev1 or the EY mutant. (C) Pol extension assay results are shown for 13/42-mer non-G4 DNA where pol κ was incubated alone or in the presence of zRev1, yRev1, or lRev1. (D) Pol extension assay results are shown for 13/42-mer G4 DNA where pol κ was incubated alone or in the presence of zRev1, yRev1, or lRev1. Product formation for each reaction was quantified and normalized against the amount of product formed in the reaction with pol κ alone. The results are shown to the right of each set of gels and represent the mean (± std. dev.) of three independent replicates. Quantification of product formation by pol κ alone is re-plotted in each panel to allow more direct comparison with the reactions containing Rev1. p-Values were calculated using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett's multiple comparisons test where *** = p-value = 0.0008, **** = p-value < 0.0001, and ns = not significant.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ RSC Chem Biol