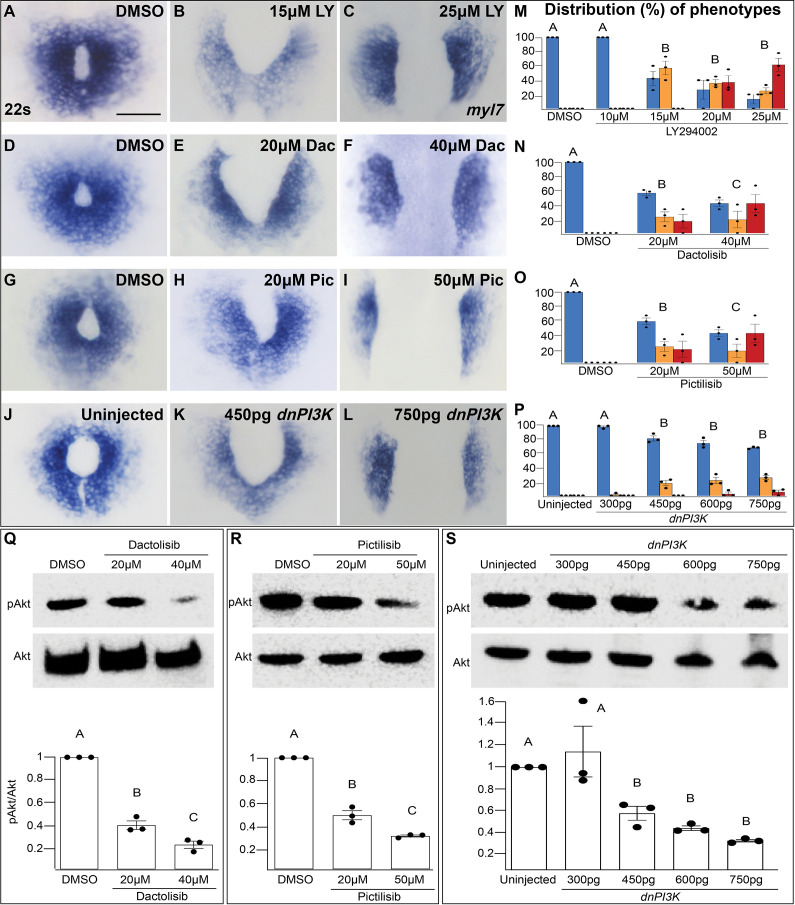
Figure 1—figure supplement 1 The penetrance and severity of cardiac fusion defects in phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-inhibited embryos is dose dependent. (A–L) myl7 insitus labeling the myocardium at 22s. Incubation with LY (A–C), Dac (D–F), Pic (G–I) from bud stage to 22s or injection with dnPI3K mRNA (J–L) at the one-cell stage results in dose-dependent cardiac fusion defects at 22s. Graphs depict the distribution of cardiac fusion defects in embryos treated with increasing concentrations of LY (M), Dac (N), Pic (O), or dnPI3K mRNA (P). Both the percent of embryos displaying cardiac fusion defects and the severity of those defects are dose dependent. Number of embryos analyzed (n) at the indicated concentrations in (M–P) LY-40, 40, 30, 31, 31; Dac: 38, 34, 39; Pic: 37, 39, 38; dnPI3K mRNA: 73, 52, 61, 57, 52, respectively. Dots indicate the percent of embryos displaying a specific phenotype per incubation. Blue – cardiac ring/normal; orange – fusion only at posterior end/mild, red – cardia bifida/severe. Bar graphs, mean ± standard error. Representative immunoblot and ratiometric analysis of phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) to Akt protein levels in DMSO and Dac (Q), Pic (R), and dnPI3K mRNA (S) treated embryos reveals a dose-dependent decrease in PI3K activation. Bar graphs indicate mean ± standard error, dots indicate pAKT/AKT ratio per biological replicate, normalized to DMSO. At least three biological replicates per treatment. Letter change indicates p < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Scale = 60 μm. Raw data with full p-values included in the source file.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife