Fig. 2
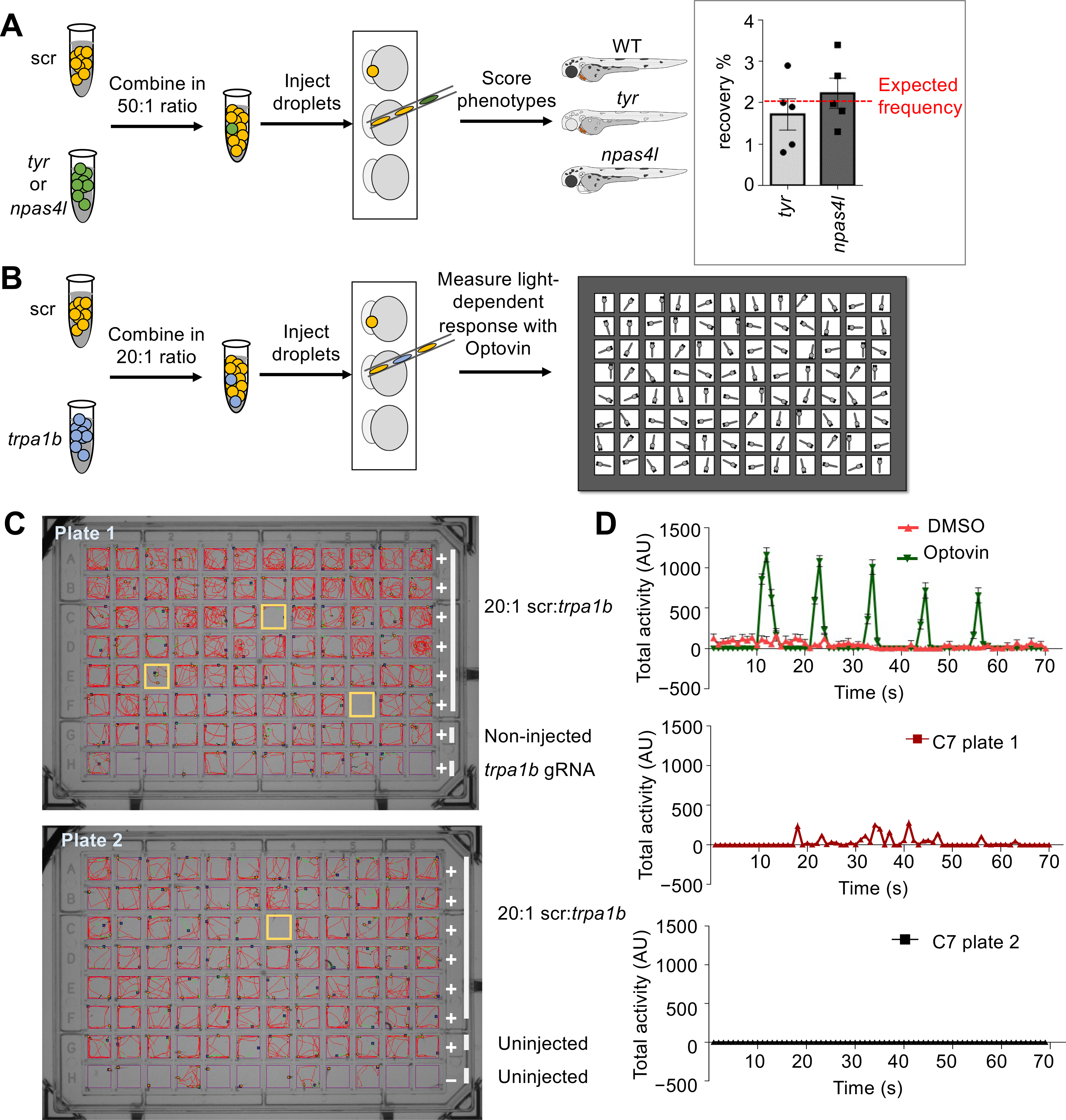
Schematic of a spike-in (A) phenotypic and (B) behavioral screen to test robustness of the MIC-Drop platform. (A) For the phenotypic screen, droplets targeting either tyr or npas4l were intermixed with droplets containing non-targeting scrambled gRNAs (scr) in a 1:50 ratio. After single-needle droplet injection, the percentage of embryos showing albino or cloche phenotypes was scored. Inset: The albino and cloche phenotypes are recovered at a frequency of ~2%, which is the expected frequency from a 1:50 ratio mix. (B) Similar to A, except droplets targeting trpa1b were intermixed with scr droplets in a 1:20 ratio. Following injection, embryos were arrayed in a multi-well plate, treated with optovin, and assayed for light-dependent motor response. (C) Tracking and (D) quantitation of zebrafish movement showed that embryos injected with droplets targeting trpa1b are refractory to optovin- and light-induced motion response.