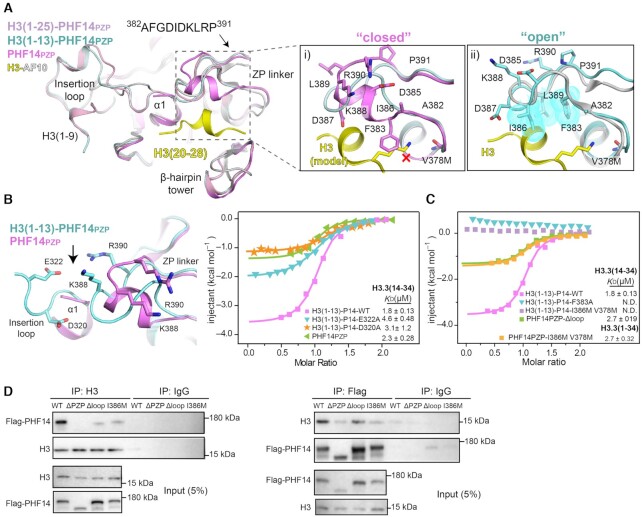
Fig. 6
Molecular basis for H3(14–34) recognition by PHF14PZP. (A) Structural alignment of PHF14PZP (magenta), H3(1–13)-PHF14PZP (pale cyan), H3(1–25)-PHF14PZP (light pink) and H3-AF10PZP (yellow-grey). Close-up views are a comparison of a ‘closed’ (i) and an ‘open’ (ii) conformation of the ZP linker. Key residues of ZP linker and H3 are shown as sticks and labelled as indicated. The red cross denotes a clash between F383 and a lysine residue of H3; hydrophobic residues are also shown as dotted spheres in cyan. (B) The interaction of insertion loop between ZP-linker region. Key residues are shown as sticks (left). ITC fitting curves of indicated H3(1–13)-PHF14PZP wild type, mutants and PHF14PZP, titrated with H3.3(14–34) peptides (right). P14 is short for PHF14PZP. (C) ITC fitting curves of indicated H3(1–13)-PHF14PZP mutants, PHF14PZP-Δloop and PHF14-I386M V378M titrated with H3.3(14–34) or H3.3(1–34) peptides. P14 is short for PHF14PZP. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation results from HEK293T cells with 3×Flag-PHF14-WT, 3×Flag-PHF14-ΔPZP, 3×Flag-PHF14-Δloop, and 3× Flag-PHF14-I386M overexpression showing bipartite recognition of the H3 tail by PHF14PZP.