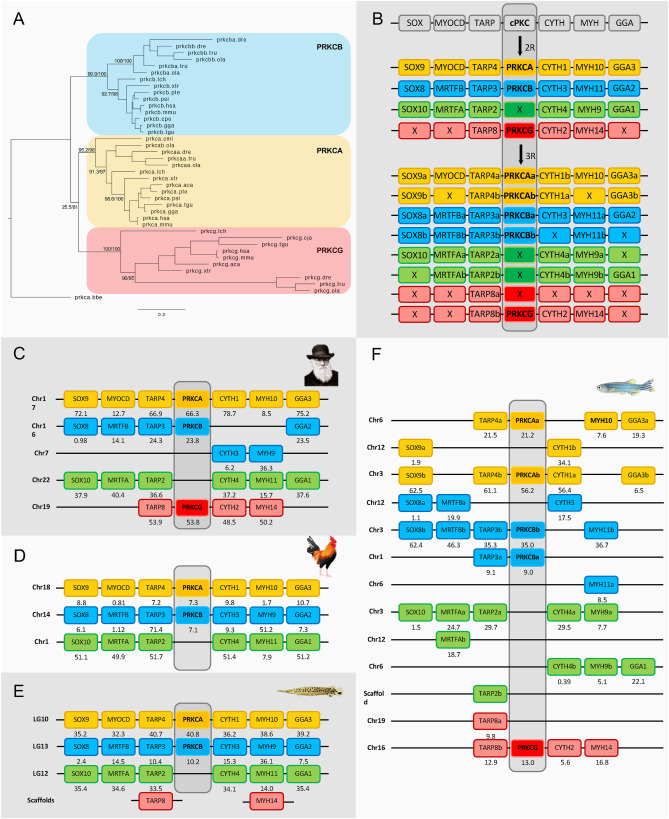
Fig. 4
Fig. 4. Phylogenetic maximum likelihood tree of the cPKC genes, rooted with the amphioxus cPKC gene (prkca.bbe) (A) after 1R, 2R and 3R (B) with chromosomal locations of the cPKC genes and their neighboring gene families in human (C), chicken (D), spotted gar (E) and zebrafish (F). Crosses indicate gene loss or gene not yet identified. The number below each gene shows the position in the chromosome. The order of the genes along the chromosomes has been adjusted to highlight the similarities. Each color field corresponds to one cPKC ohnolog. PRKCG was found in the chicken as a pseudogene and thus it was not included in the analysis. The tree topology is supported by a non-parametric Ultra-Fast Bootstrap (UFBoot) analysis. The full tree values in Newick format file can be downloaded as supplementary material.Chicken and spotted gar illustrations are re-used with permission from Daniel Ocampo Daza, source: https://www.egosumdaniel.se and the human image is used with permission from https://commons.wikimedia.org. This paralogon is referred to as paralogon I in this study.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 479, Garcia-Concejo, A., Larhammar, D., Protein kinase C family evolution in jawed vertebrates, 77-90, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.