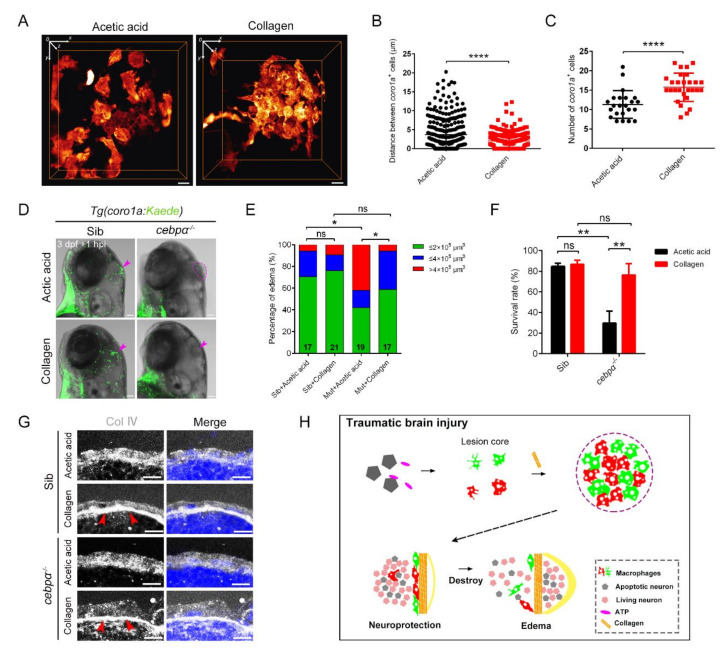
Fig. 8
Collagen was crucially involved in the construction of the honeycomb network structure and the protection of brain integrity. (A) The distribution of macrophages after collagen/acetic acid injection in Tg(coro1a:DsRed) embryos at 1 hpi. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Statistical analysis of distances between the coro1a-DsRed+ cells in (A). Acetic acid, 3.73 ± 0.21 µm n = 340; collagen, 2.05 ± 0.10 µm n = 351. Acetic acid, collagen solvent. (C) Statistical number of aggregated coro1a+ cells in (A). Acetic acid, 11.30 ± 0.75 n = 23; collagen, 15.75 ± 0.69 n = 28. (D) The bright field and fluorescent images of coro1a-Kaede+ cells and edema-like symptoms (purple arrowheads and dashed line) in sibling and cebpα mutant with collagen/acetic acid injection. Scale bar, 100 µm. (E,F) Statistics of edematous symptoms (E) and survival rate (F) after collagen/acetic acid injection in cebpα mutant and sibling. (G) The immunofluorescence staining of collagen (Col Ⅳ) in cebpα mutant after injection of collagen. Scale bar, 10 µm. Red arrowheads indicate dense collagen layers. (H) Diagram of our results. The rapid and efficient construction of the honeycomb network structure by aggregated macrophages/microglia required nucleotide-mediated migration and collagen supportive tight junctions. The honeycomb network structures played an important role in the integrity of the damaged brain to protect the brain components inside. (Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ns, no significance; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001.)